File - OTHS Aquatic Science
advertisement

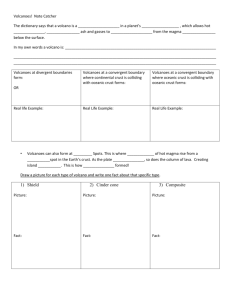
Key Geological Features Test Review Define the following: 1. Trench-deepest part of the oceans, located on the edge of convergence zones 2. Submarine canyon- a deep canyon cut into the continental shelf and slope 3. Continental slope- the part of the ocean that connects the continental shelf to the ocean basin that is characterized by a drastic change in depth 4. Seamount- an isolated undersea hill or mountain 5. Continental Margin- shallow water areas close to the continents 6. Island chain- a group of islands formed by the same geological process 7. Bay-inlet of the sea 8. Atoll- a ring shaped coral reef surrounding a lagoon; it may have low 9. Passive Margin- continental margin with a low degree of tectonic activity 10. Peninsula-a piece of land almost completely surrounded by water 11. Continental Shelf- submerged part of the continent forming the shallow seafloor extending outward from the edge of the continent 12. Guyot- seamount with a flat top 13. Abyssal plain- flat surface extending seaward from the continental rise 14. Active Margin- continental margin with a high degree of tectonic activity Labeling: - Be able to label the following on a map Submarine Canyon Continental Shelf Bay Headland/cape Island Delta Continental Slope Questions: 1. Which ocean is getting bigger and why? Atlantic; divergent boundaries 2. Which ocean is getting smaller and why? Pacific; convergent boundaries 3. What boundaries create new oceanic crust? Divergent boundaries 4. What boundaries destroy oceanic crust? Convergent boundaries 5. What is the driving force behind plate tectonics? Convection currents 6. Where does seafloor spreading begin? Rift valleys 7. How is the mid-ocean ridge formed? Divergent boundaries 8. How is a trench formed? Convergent boundaries 9. How were the Aleutian Islands formed? Oceanic-oceanic convergent boundaries 10. How was Hawaii formed? Hot spots 11. Where is the International Date Line located? 180 12. How is longitude read? East or west of prime meridian 13. What is the primary reference line for latitude? equator 14. How is latitude read? North or south of the equator 15. What is the primary reference line for longitude? Prime meridian 16. What is a divergent boundary? Where new crust is formed by sea floor spreading 17. What is a characteristic/main feature of a divergent boundary? rift 18. What is a convergent boundary? When two plates collide 19. What is a characteristic/main feature of a convergent boundary? Subduction zone with a trench; volcanoes 20. What are the types of convergent boundaries discussed in class? Oceanic-oceanic; oceanic-continental 21. Which crust is denser? Oceanic crust 22. Which crust is less dense? Continental crust 23. In an island chain which island is the “youngest” and which island is the “oldest”? youngest close to hot spot; oldest furthest away from hot spot 24. What mechanism creates a ridge? Sea floor spreading 25. In the Atlantic, which part of the oceanic crust is younger? Closest to ridge 26. In the Atlantic, which part of the oceanic crust is older? Farthest from ridge; near continent 27. What does the topography look like at active margins? Chains of islands; deep sea trenches; thin sediment; volcanic and earthquake activity 28. What does the topography look like at passive margins? Broad continental shelves; shallow coastal waters; thick sediment accumulation; very little volcanic and earthquake activity 29. List everything associated with a divergent boundary. Rift valley; seafloor spreading 30. List everything associated with a convergent boundary. Oceanic- oceanic; oceanic-continental; island arc; trench ; volcanoes