Crustal Features and Plate Boundaries
advertisement

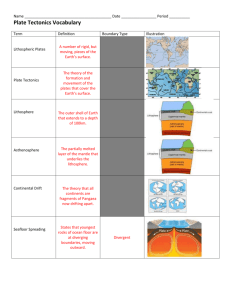
Crustal Features and Plate Boundaries Notes Subduction zones -occur where an oceanic plate meets a continental plate and is pushed underneath it. These zones are a type of convergent boundary. Ocean plates are denser than continental plates, so the oceanic plate is pushed under the continental plate. Subsidence- is a lowering in elevation of land. This lower area usually fills in with water. **LAND FEATURES…. Trench – a deep depression of the sea floor caused by the subduction of one plate under another (convergent) Rift Zones – a large valley shaped area of the earth in which plates of the earth's crust are moving away from each other, forming a system of cracks and faults (divergent) Oceanic Ridges – underwater mountain ranges where the crust is spreading creating new ocean floor (divergent) Underwater Mountain Ranges – long, continuous volcanic chain of various mountain ranges (divergent) rising from the ocean floor Mountain Ranges on Land – a series or chain of mountains that are close together and rise 300 m (1,000 ft.) above its surrounding area (convergent) Ring of fire – volcanoes that are concentrated on the edges of continents, along island chains, or beneath the sea forming long mountain ranges. More than half of the world's active volcanoes above sea level encircle the Pacific Ocean to form the "Ring of Fire." (convergent) Fault- a break in the rocks that make up the Earth’s crust, this occurs when two plates move past one another. (transform)