Mr. Freidhoff`s Keystone Study Guide (2 nd Edition)
advertisement

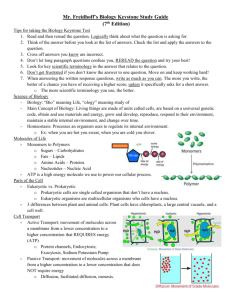
Mr. Freidhoff’s Keystone Study Guide (2nd Edition) Tips on taking the Biology Keystone Test 1. Logically think about what the question is asking for. Apply the answers to the specific question. 2. Don’t let long paragraph questions confuse you, REREAD the question and answer to the best of your ability. 3. Cross off answers you know are incorrect. 4. Look for key scientific terminology in the answer that relates to the question. 5. Don’t get frustrated if you don’t know the answer to one question. Move on and keep working hard! 6. When answering the written response questions, write as much as you can. The more you write, the better of a chance you have of receiving a higher score. o Use scientific terminology in your answer. Major Concepts 1. Monomers to Polymers o Sugars – Carbohydrates o Fats – Lipids o Amino Acids – Proteins o Nucleotides – Nucleic Acid 2. Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic o Prokaryotic cells are single celled organisms that don’t have a nucleus. o Eukaryotic organisms are multicellular organisms that have a nucleus. 3. Cell Cycle o Cell Cycle o Interphase: G1, S, G2 o Mitotic phase: Mitosis, Cytokinesis o Mitosis o All cells divide by this process o Creates two genetically identical daughter cells o Creates two diploid cells (2n) 4. Meiosis o Sex cells divide in this process o Creates 4 genetically different daughter cells o These four cells are haploid (n) 5. 3 differences between plant and animal cells: Plant 6. 7. 8. 9. cells have chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell well. Abiotic is a non-living factor in an ecosystem, biotic factors are living factors. ATP is a very important molecule that contains the energy we use to function. o ATP = Energy Lipids are hydrophobic, Carbohydrates are hydrophilic Homeostasis: Processes an organism uses to regulate its internal environment. o Example: when you are hot you sweat, when you are cold you shiver. Enzymes - Enzymes are large molecules that speed of rates of reaction (catalysts) - Enzyme (large molecule) acts as a lock, while the substrate that is change acts like its key. DNA/RNA 1. Nucleotides are made up of three parts: Nitrogenous base, phosphate group, 5-carbon sugar 2. DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded 3. Central Dogma of Molecular Biology - DNA →RNA →Proteins Genetics - - - - Gene: a discrete unit of hereditary information that usually specifies a protein; a region of DNA located on a chromosome that specifies a trait Genotype: the genetic make-up of an individual. Phenotype: the physical or chemical expression of an organism’s genes. Dominant allele: (Capital Letter: A) an allele that is always expressed when present, regardless of whether the organism is homozygous or heterozygous for that gene. Recessive allele: (Lower case Letter: a) an allele that is only expressed when the organism is homozygous for that allele and not expressed when heterozygous (when paired with a dominant allele). Homozygous: possessing a pair of identical alleles for a particular locus (gene). Heterozygous: possessing a pair of unlike alleles for a particular locus (gene). Mutation: Error in the genetic code, sometimes creates a new phenotype. Haploid: the condition of having only one set of chromosomes per cell (n) Diploid: the condition of having two sets of chromosomes per cell (2n) Evolution - Natural occurrence of CHANGE OVER TIME! o Occurred over billions of years - Mutations lead to changes in the phenotype - Explained by Charles Darwin o Went on voyage upon the HMS Beagle to South America, Africa, and Galapagos Islands o Worked with Finches, tortoises, and barnacles o Wrote On the Origin of Species - Natural Selection o Mechanism of Evolution o Organisms with “bad” genes won’t make it to reproduction age while organisms with “good” genes will reproduce more Cell Transport - Active Transport: movement of molecules across a membrane from a lower concentration to a higher concentration that REQUIRES energy (ATP) o Protein channels, Endocytosis; Exocytosis, Sodium Potassium Pump - Passive Transport: movement of molecules across a membrane from a higher concentration to a lower concentration that does NOT require energy o Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis. Scientific Terminology - Hypothesis: An educated guess about something, Based on observations, Testable - Scientific Theory: use to synthesize a body of evidence or observations of particular phenomena. Can build upon a theory with new knowledge and experiments. - Scientific Law: A law generalizes a body of observations. At the time it is made, NO exceptions have been found to a law. - In order of most scientifically proven to least scientifically prove. o Law > Theory > Hypothesis Life Processes - Cellular Respiration: Process where chemical energy is converted to ATP in the Mitochondrion o C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Energy - Photosynthesis: Process where light energy is combined with CO2 and H2O to create sugar molecules o CO2 + H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + O2 nucleus chromosomes mitochondria ribosome’s endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus lysosome chloroplast cell membrane cell wall eukaryote prokaryote vacuole Cell Organelles the control centre of the cell genetic material found in the nucleus where energy in the form of ATP is produced where proteins are made transport system in the cell packages up protein special type of vacuole that breaks down large molecules and cell parts where photosynthesis occurs semi-permeable; it controls what moves in and out of the cell protects and supports plant cells cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus a cell with no nuclear membrane and few (if any) membrane bound organelles stores wastes, water, food GOOD LUCK!