8. Cell – Structure and Functions - Suresh Dod
advertisement
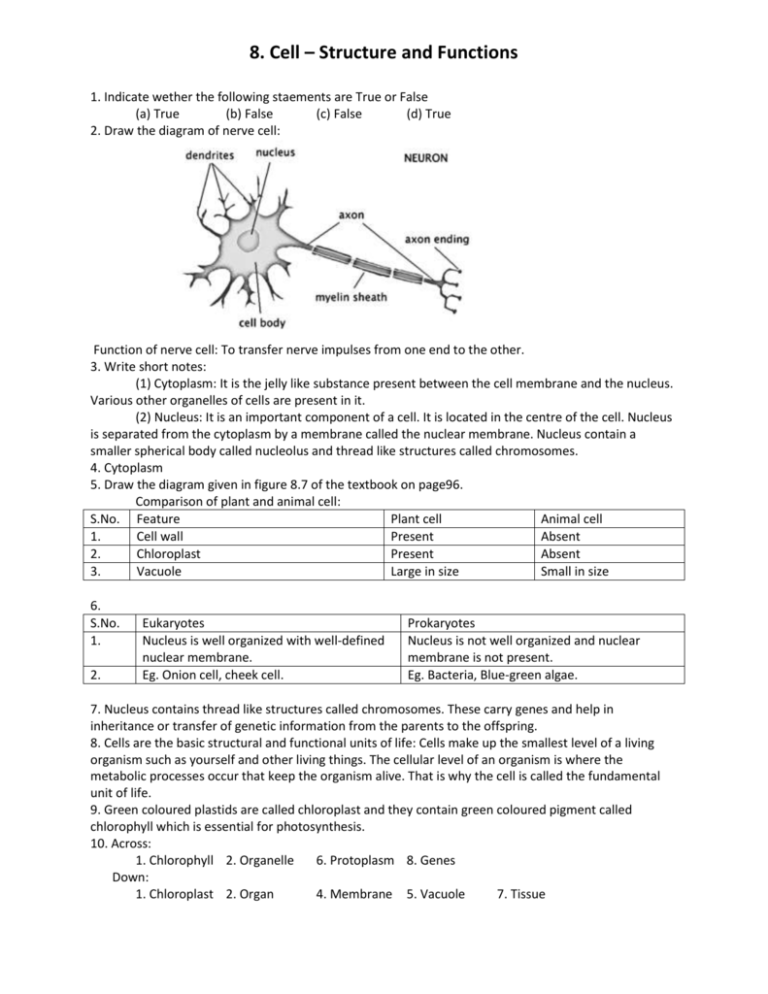
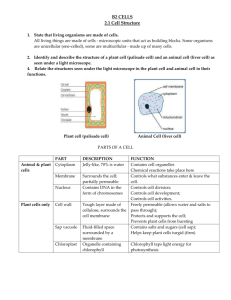
8. Cell – Structure and Functions 1. Indicate wether the following staements are True or False (a) True (b) False (c) False (d) True 2. Draw the diagram of nerve cell: Function of nerve cell: To transfer nerve impulses from one end to the other. 3. Write short notes: (1) Cytoplasm: It is the jelly like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various other organelles of cells are present in it. (2) Nucleus: It is an important component of a cell. It is located in the centre of the cell. Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. Nucleus contain a smaller spherical body called nucleolus and thread like structures called chromosomes. 4. Cytoplasm 5. Draw the diagram given in figure 8.7 of the textbook on page96. Comparison of plant and animal cell: S.No. Feature Plant cell Animal cell 1. Cell wall Present Absent 2. Chloroplast Present Absent 3. Vacuole Large in size Small in size 6. S.No. 1. 2. Eukaryotes Nucleus is well organized with well-defined nuclear membrane. Eg. Onion cell, cheek cell. Prokaryotes Nucleus is not well organized and nuclear membrane is not present. Eg. Bacteria, Blue-green algae. 7. Nucleus contains thread like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of genetic information from the parents to the offspring. 8. Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life: Cells make up the smallest level of a living organism such as yourself and other living things. The cellular level of an organism is where the metabolic processes occur that keep the organism alive. That is why the cell is called the fundamental unit of life. 9. Green coloured plastids are called chloroplast and they contain green coloured pigment called chlorophyll which is essential for photosynthesis. 10. Across: 1. Chlorophyll 2. Organelle 6. Protoplasm 8. Genes Down: 1. Chloroplast 2. Organ 4. Membrane 5. Vacuole 7. Tissue