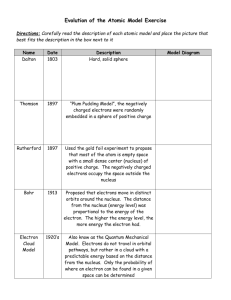
8th Grade Science Mid term study guide
advertisement
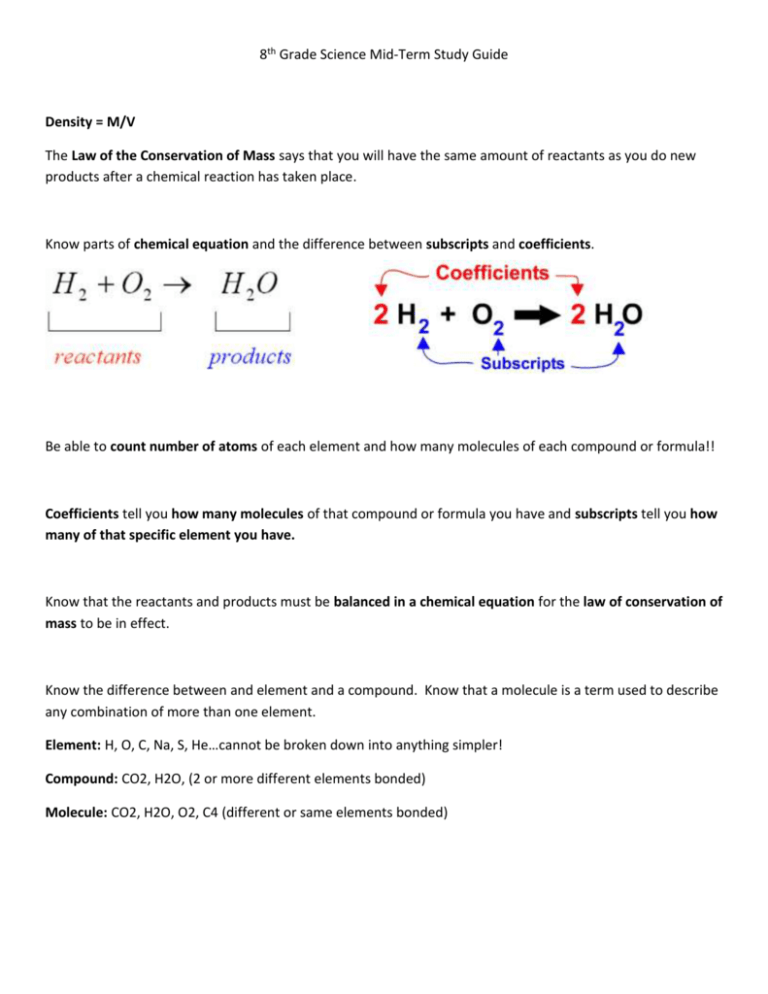
8th Grade Science Mid-Term Study Guide Density = M/V The Law of the Conservation of Mass says that you will have the same amount of reactants as you do new products after a chemical reaction has taken place. Know parts of chemical equation and the difference between subscripts and coefficients. Be able to count number of atoms of each element and how many molecules of each compound or formula!! Coefficients tell you how many molecules of that compound or formula you have and subscripts tell you how many of that specific element you have. Know that the reactants and products must be balanced in a chemical equation for the law of conservation of mass to be in effect. Know the difference between and element and a compound. Know that a molecule is a term used to describe any combination of more than one element. Element: H, O, C, Na, S, He…cannot be broken down into anything simpler! Compound: CO2, H2O, (2 or more different elements bonded) Molecule: CO2, H2O, O2, C4 (different or same elements bonded) Subatomic particles are the Electron, Proton and Neutron. They make an ATOM! Electron has NEGETIVE CHARGE and lives in the energy rings or electron cloud around nucleus. Proton has POSITIVE CHARGE and lives in the nucleus of atom (center) Neutron is NEUTRAL HAS NO CHARGE and lives in nucleus with proton An element is identified by its Atomic Number. The atomic number is the number of Protons and electrons the element has. Valence electrons are electrons in outer most energy level ONLY!! They determine reactivity of the elements in the same group!! Why are elements in the same group on the table? Because they have similar properties and similar reactivity!!!!! They have the same number of electrons. periodic valence Periods on the periodic table go across and those elements have the same number of electron/energy shells/levels. Bohr Models show energy levels and the amount of electrons in each level Know the characteristics of Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids: Time Distance Graph: Average Speed= total distance/total time Speed Time Graph: Physics formulas: Speed Velocity and Acceleration: Signs of a Chemical reaction: 1. New product is formed 2. Gas is released – bubbles form 3. Precipitate forms (solid forms in liquid) 4. Temperature change (hot – exothermic/cold – endothermic) 5. Energy is released (light or sound) Know Potential and Kinetic energy! Newton’s 3 Laws: 1. First Law – Law of Inertia: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force." Objects tend to "keep on doing what they're doing." In fact, it is the natural tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of motion. This tendency to resist changes in their state of motion is described as inertia. 2. Newton’s Second Law: Objects acceleration is dependent upon the mass of the object and the force applied to it. 3. Newton’s Third Law: Every action has an action of equal force but opposite direction. When is work being done? Remember!!!!! Objects with more mass have more inertia Objects with less mass have more acceleration Net forces: the total amount of force applied to an object. This cart will move to the right with a force of 40N. Know how to find the direction and magnitude (amount) of force! Law of Conservation of Energy: No new energy is created or destroyed; it is only transferred from one form to another. **See the examples of energy transfers you had on the review!!!