What is an Earthquake?
advertisement
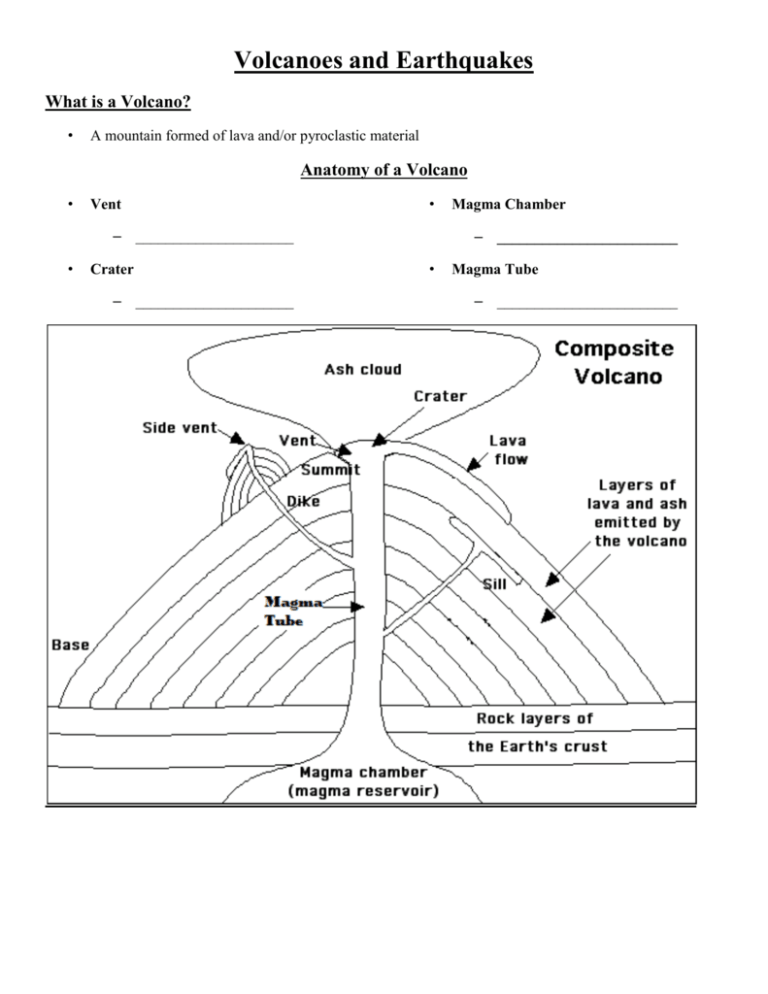
Volcanoes and Earthquakes What is a Volcano? • A mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic material Anatomy of a Volcano • Vent • – _____________________ • Crater – _____________________ Magma Chamber – ________________________ • Magma Tube – ________________________ Types of Volcanoes • Determined by – _________________________ – _________________________ • 3 types – Shield Volcano • _____________________ • _____________________ • _____________________ • _____________________ • _____________________ • ________________________ ________________________ • ____________________ – Cinder-Cone Volcano • _______________ • __________ – Composite Volcano • Also known as ___________ • _________________ • Large, nearly ____________ _____________ • _________________ • Ex: ______________ • Layers of lava and ____________________ Magma verse Lava • • Magma Lava – __________________________ __________________________ – _________________________ Factors Affecting Eruption • ______________________ • ______________________ • ______________________ Viscosity of Magma • _________________________ • _________________________ ___________________ • _______________________________ – ________________________ ________________________ Dissolved Gases • Consist of _________________________ • More gases, ________________________ Volcanic Materials • Lava Flow – Pahoehoe: __________________________________ – Aa: ________________________________________ • • Gases – 70% _____________ – 5% _________ – 15% _____________ – 5% ________ Pyroclastic Material – Fragments ejected during eruptions – From very fine to several tons – Ex: • Volcanic Ash • Cinders (lapilli) • Other Eruption Results • Pyroclastic Flow – ______________________________________ – ______________________________________ • Lahar – __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Volcanic Landforms • Calderas – _______________________________ – Forms Two Ways • _______________________________________________ Volcanic Bombs • • ________________________________________________ Lava Plateaus – _________________________ – ______________________________________________ Intrusive Igneous Activity • This is also known as ___________________ • Plutons – Structures that result from the _____________________________________ – Classified according to _____________________________________________ – Types of Plutons • • • • Sills • • ______________ __________________ __________________ __________________ Laccoliths __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ Dike • __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ Batholith • __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ Plate Tectonics & Volcanoes • Relationship – ______________________________________________________________________ Ring of Fire • • _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Intraplate Activity • • Occurs with a plate, not a plate boundary Hot Spots – ______________________________ – ______________________________ What is an Earthquake? • _____________________ • ___________________ • ___________________ Parts of an Earthquake • • • Focus – _______________________________________ Epicenter – _______________________________________ Fault – _______________________________________ Causes of Earthquakes • Elastic Rebound Hypothesis – Release of built-up energy – Most earthquakes are produced by the rapid release of elastic energy stored in rock that has been subjected to great forces – When the strength of the rock exceeded, it suddenly breaks, causing the vibrations of an earthquake Foreshock vs. Aftershock • Foreshock – ______________________________ __________ • Seismology – ______________ ______________ ______________ • Aftershock – ______________________________ __________________ Seismic Science • Seismograph __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Earthquake Waves • Two Main Types – Surface Waves – Body Waves • P-waves • S-waves Surface Waves • • ____________________________________ ____________________________________ __________________________________ • • ___________________ ___________________ Body Waves • • P-Waves (primary waves) – They push (compress) and pull (expand) rocks in the direction the wave travels – Can travel through _________________________ – ____________________ – ____________________ S-Waves (secondary waves) – Shakes particles at ______________ to their travel – Can only travel through __________ – _____________________ Locating Earthquakes • The difference in velocity of a P-Wave & S-Wave provides a way to locate the epicenter – ____________________________ – ____________________________ Strength of an Earthquake • Two different types of measurements to describe the strength of an earthquake – _______________ – _______________ • ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Earthquake Intensity Earthquake Magnitude • ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ The Richter Scale • • • • _____________________ Based on the amplitude of the ___________________ A ______________ system Largest earthquake record= _____________ Moment Magnitude Scale • • More precise Amount of displacement that occurs along a ________________ • Most widely used – ______________________________ ______________________________ Mercalli Intensity Scale • • How much damage occurs Depends on: – ____________________ – ____________________ – ____________________ – ____________________ Earthquake Hazards • • Seismic Vibrations – Damage to building depends on several factors • ___________________________ • ___________________________ • ___________________________ • ___________________________ Liquefaction – Stable soil turns into a _________________________________________________ • • • Tsunami – _________________________________________ – Tsunami warning system is active to monitor for them Landslides – ______________________________ – Sinking of the ground triggered by the _________________ Fires – Caused by ______________________ Predicting Earthquakes • • Short Range – _________________________________________ – Short-range predictions has not been successful Long Range – _______________________________________ – Seismic Gap • ________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________