Earthquakes and Volcanoe notes - key
advertisement

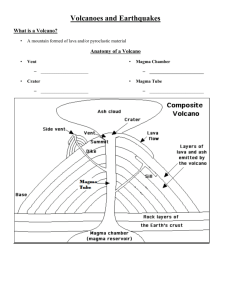
Earthquakes & Volcanoes Earthquakes • Occur mostly at boundaries of tectonic plates • Stress of moving plates becomes so great it breaks rock •Seismic waves – energy released from shifting. Produces shaking • Focus – exact point inside the earth where the earthquake originates. • Epicenter – the point on the surface of the earth directly above the focus. 3 types of waves 1. __P or Primary waves___________________ • Originate at the focus • move faster than other waves • they are longitudinal waves 2. _____S – secondary waves________________ • Originate at the focus • Travel more slowly than P waves • They are transverse waves 3. __Surface Waves_____ • Move only across the earth’s surface • Cause the most destruction • Generates rolling action at the earth’s surface Seismology • Study of earthquakes. • Seismograph – instrument that detects earthquakes. • 3 seismograph stations are necessary to locate the epicenter of an earthquake. Richter Scale – describes the amount of energy an earthquake has, cannot predict amount of damage that will occur Volcanoes • Any opening in the earth’s crust through which magma has reached • Vent – term for opening in the earth • Lava – magma that has reached the earth’s surface. • There are 3 types Shield Volcanoes • fluid iron and magnesium rich magma • mild eruptions which happen many times • form some of the largest volcanoes • Examples Mauna Loa, Haleakala Composite Volcanoes • Alternating layers of ash, cinder, and lava • thick ,lava, rich in silica • trapped gas causes eruptions to alternate between lava flows and explosive activity that produces cinders and ash • Examples Mt. Fuji Cinder Cone • smallest and most abundant • lava contains large amount of gas. Causes eruptions with a large amount of ash. • active for only a short period of time, then go dormant • Examples Paricutin