C2S3-and-C2S4--study
advertisement

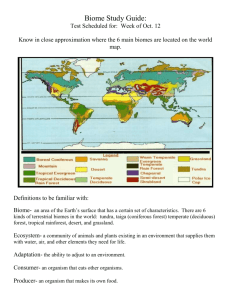
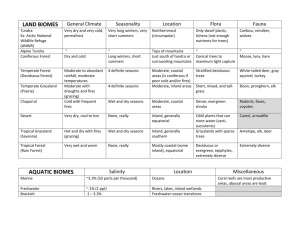
Name: _______________________ B___ Date:______________ Test Date: _________ Study Guide Chapter 2 Section 3: Biography- Textbook pages 54-57 Chapter 2 Section 4: Biomes pages 58-67 biogeography- the study of where organisms live continental drift- the very slow motion of the continents dispersal- the movement of organisms form one place to another exotic species- species that are carried to a new location by people climate- typical weather pattern in an area over a long period of time List 3 ways organisms can be dispersed 1. wind 2. water 3. living things biome- A group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms canopy- A leafy roof formed by tall trees in a forest understory- A layer of shorter plants that grow in the shade of a forest canopy desert- An area that receives less than 25 centimeters of precipitation per year grassland- An area populated by grasses an and other nonwoody plants. Most grasslands get 25 to 75 centimeters of rain each year savanna- A grassland close to the equator that receives as much as 120 centimeters of rain per year deciduous forest- A forest where the trees shed its leaves and grows new ones each year coniferous forest- A forest where the trees produce its seeds in cones and that has needle-shaped leaves boreal forest- Forest filled with firs and spruces trees. These trees are coniferous tundra- An extremely cold, dry biome permafrost- Solid that is frozen all year 6 Major Land Biomes: 1. rainforest 2. deciduous forest 3. boreal forest 4. grasslands 5. tundra 6. desert