Biome Study Guide: Definitions, Adaptations, and Locations
advertisement
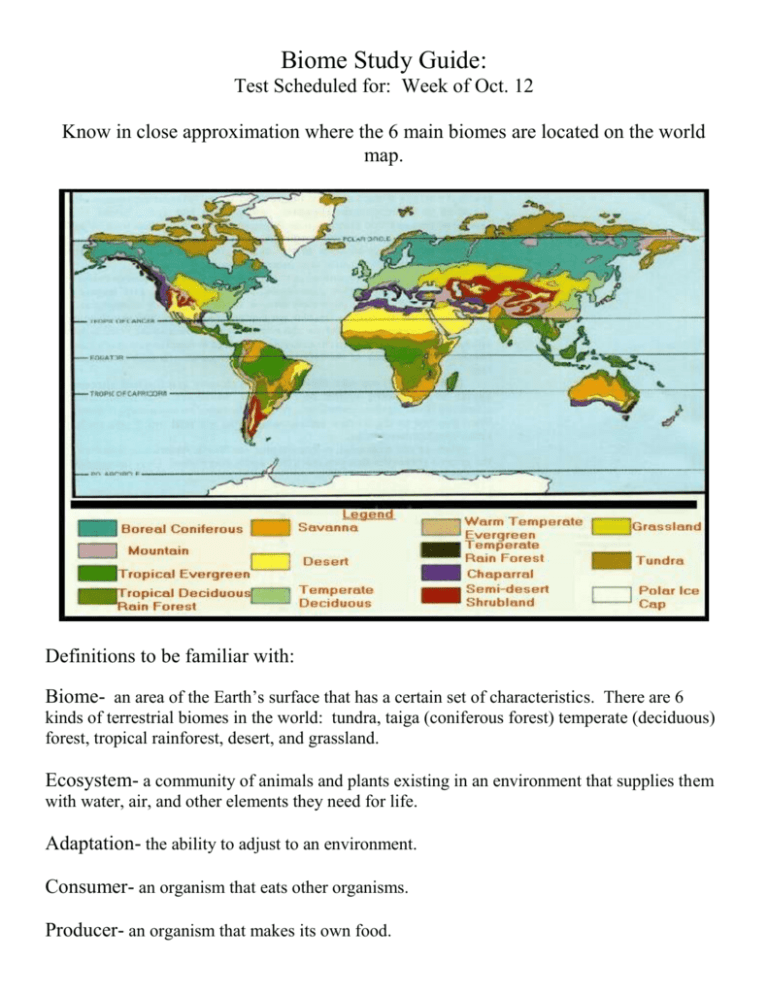
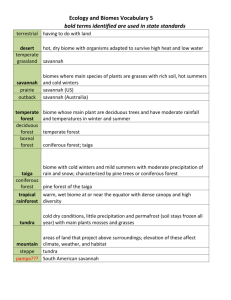
Biome Study Guide: Test Scheduled for: Week of Oct. 12 Know in close approximation where the 6 main biomes are located on the world map. Definitions to be familiar with: Biome- an area of the Earth’s surface that has a certain set of characteristics. There are 6 kinds of terrestrial biomes in the world: tundra, taiga (coniferous forest) temperate (deciduous) forest, tropical rainforest, desert, and grassland. Ecosystem- a community of animals and plants existing in an environment that supplies them with water, air, and other elements they need for life. Adaptation- the ability to adjust to an environment. Consumer- an organism that eats other organisms. Producer- an organism that makes its own food. Decomposer (detrivore)- an organism that breaks down dead plant and animal material. Ecological Relationship- the relationship between organisms in an ecosystem with each other, the ecosystem, and the ecosystem itself with other ecosystems. All populations living together within a community that interact with one another and with their environment in order to survive and maintain a balanced ecosystem. Temperate (deciduous) Forest- a forest consisting mostly of deciduous trees growing in regions with moderate temperatures. They are usually located north and south of tropical forests. Tropical Rainforest- forests in which there is more than 80 inches of rainfall per year. The temperatures are warm to hot year round and exist mainly near the equator. Desert- an area, either hot or cold, where the annual precipitation is less than 10 inches a year. The plants and animals that live here are highly adapted to live in these dry areas. Tundra- the name “tundra” comes from a Finnish word meaning “treeless plain.” It is found at high latitudes (arctic tundra) and at high altitudes (alpine tundra). Arctic tundra has permanently frozen subsoil. Plants are very low growing, like mosses, lichens, grasses, and some dwarf woody herbs. Temperatures are very cold in winter- summers are short and cold. Taiga (coniferous) Forest- an area characterized by coniferous (cone bearing) trees. They are located just south of the tundra and have an annual precipitation of 15-40 inches per yearusually snow. Taiga is also called a Boreal forest. Summers are cool- winters are cold. Grassland- an area dominated by grasses and very few trees. There is a moderate annual rainfall between 10-30 inches- enough to support the growth of grasses and small plants, but not enough to support trees. They are sometimes called a “prairie.” There are “short” and “tall” grasslands, depending on the amount of precipitation they get. Grasslands usually have cold winters, a rainy spring, and a dry, hot summer. How have plants and animals adapted to their environments? *Plants adapt so they can get as much sunlight, and water as possible for making food. What are some ways that plants adapt? (length of root, wide, flat leaves, grow close to the soil so their stems don’t break in a windy area, hair on their stems help hold in water, waxy coating, colorful blossoms to absorb more of the sun’s rays etc.) Be able to describe how a plant from each biome adapts. *Animals adapt also: (body covering, ears, fur, armor, weaponry, camouflage, hibernation, strength, speed, dormant): Be able to describe how an animal from each biome adapts. Food Chain: the path by which energy passes from one living thing to another. Food Web: several food chains that are connected Green plants are called producers because they have the ability to make their own food that the consumers eat. Consumers that only eat plants are called herbivores Consumers that only eat meet are called carnivores Consumers that eat both meat and plants are called omnivores