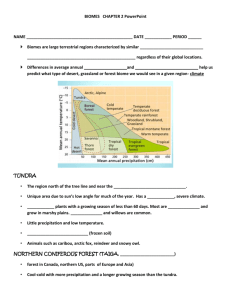
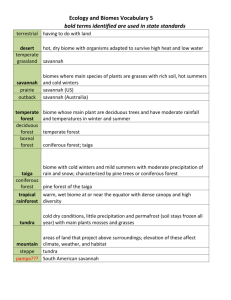
Chapter 20 Study Guide Section 1 P and t are the main factors that
advertisement

Chapter 20 Study Guide Section 1 1. P and t are the main factors that determine what kind of biome is found in a region. 2. The three main types of forests are t c d , and the t , r f 3. The nonliving factors of an ecosystem are called a 4. A b . . is a geographic area characterized by certain types of plant and animal communities. 5. Biomes contain a number of smaller e . 6. If there is enough rain and the temperatures are not too cold or hot, f biomes occur in the area. is term that means “to fall off” and in the southern U.S. it refers to 7. D the leaves falling from the trees in the fall. 8. The t d forest occurs in the North Georgia area. 9. The animals found in the type of forest referred to in question number 8 include D , sq , and r 10. The c (name 3). forest is characterized by trees that produce cones. trees, which do not lose their “leaves” 11. The cone bearing forests have e needles during the year. 12. The floor of the coniferous forest is almost void of plants because light from the sun does not reach the forest floor. 13. The forest biome that has more biological diversity than other forests is the T R F . 14. The upper layer of a forest where you find the treetops is called the c 15. Most of the nutrients in the tropical rain forest are tied up in the pl . . 16. The soil in the tropical rain forest is very nutrient poor. How many years can farmers grow crops on the land if they clear the forest? T . 17. The biome found between deserts and forests are g . 18. In the United States, we have t grasslands. 19. One of America’s largest herbivores that we read about is the b , which some people call buffalo. 20. In Africa, we find the grassland called the s herbivores on it. , which has zebras and other 21. The t roots of plants enable them to survive during the drought. 22. D are hot, dry regions that support a variety of plants and animals. 23. Many animals avoid the heat of the desert by being active at n 24. Some plants have numerous widespread r desert, while others have a t . to absorb the water when it rains in the root that extends down to ground water. 25. The biome that is found in the far north and the high tops of the mountains where no trees grow is the t . 26. In the Arctic tundra the ground is frozen all year long below 12 to 18 inches. This is called the p . 27. List a few examples of the animals you could see if you visited the arctic tundra. 28. Tundra that occurs above the tree line on mountains is called A tundra. Section 2 Study Guide. 1. Marine biomes are also shaped by a factors. 2. The most abundant producers in the ocean are p . 3. The most abundant producers in the oceans are eaten by organisms called Z . 4. Describe the four zones of the ocean beginning with the shallowest zone and proceeding to the deepest zone. Include examples of the organisms you would find there. 5. In clear sunny, tropical warm waters we often find c reefs. 6. What is a characteristic of the organisms that we find at these reefs. Br C . 7. The algae called Sargassum gives the sea in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean its name. What sea are we talking about? S sea. 8. What form or adaptation does many of the organisms in this sea use to avoid predation? Ca . 9. The A Y Ocean is where we find polar ice. Are these waters rich in nutrients? . 10. An area where freshwater and saltwater meet is called an e 11. The base of the food chain in aquatic ecosystems must be p all aquatic ecosystems where light can penetrate. . because it grows in 12. How do organisms keep from being washed away in the Intertidal zone? Name a few organisms found here. W ,C , Cl . SECTION 3 FRESHWATER ECOSYSTEMS 1. There are two types of freshwater ecosystems, what are the two broad categories? Mo water and s water. 2. The small streams that enter into larger streams are called t of the larger stream. 3. When the current flow slows down and sediment settles out of s stream or river, a D is often formed. 4. All moving water empties into a l or an o . 5. The bodies of water that do not move have a zone called the l zone that is close to the land and may have cattails growing there. 6. Away from the littoral zone we find the o water zone where the plants do not grow because it is too deep, but plankton grow where the sunlight penetrates. 7. From where do organisms in the deep-water zone get their food? They often get their food from the b because they are often bottom feeders. 8. Name a few organisms that survive in the deep-water zone. 9. A w is an area of land that water is near or above the surface of the land for most of the year. 10. A m is a treeless wetland ecosystem that often has cattails and rushes growing. (Some may say it is flooded grassland). 11. A wetland with trees that are flooded during a portion of the year or all year is called an s . (Some may say it is a flooded forest). 12. Explain how a body of water can eventually “vanish” and result in a forest. In other words, how could a local pond end up a temperate deciduous forest after many years of succession?