Study Guide Nuclear Chemistry Vocabulary: o Alpha particle o Beta
advertisement

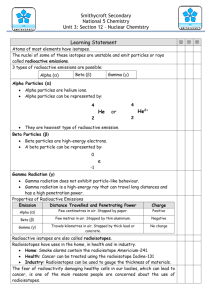
Study Guide Nuclear Chemistry Vocabulary: o Alpha particle o Beta particle o Binding Energy o Fission o Fusion o Gamma ray o Geiger counter o Half-life o Isotopes oMass Defect oNulcear Fission oNuclear Fusion o Nuclear force o Radiation o Radioactive decay o Radioisotopes o Transmutation 1. How does an unstable nucleus release energy? By emitting radiations during radioactive decay 2. What does it mean if something is radioactive? What causes something to be radioactive? Something that has a spontaneous emission of a stream of particles or electromagnetic rays as it decays. Unstable nucleus 3. Explain the Nuclear stability. Discuss the stable neutron to proton ratios. Nuclear stability means that nucleus is stable meaning that it does not spontaneously emit any kind of radioactivity (radiation). On the other hand, if the nucleus is unstable (not stable), it has the tendency of emitting some kind of radiation, i.e., it is radioactive. Therefore the radioactivity is associated with unstable nucleus. Stable n/p ratio for small atoms – 1:1 Stable n/p ratio for large atoms-1.5:1(You have more neutrons) 4. What are the three main types of nuclear radiation? Alpha, Beta and Gamma 5. Describe the mass, charge, actual identity, and relative penetration power of the following radioactive particles: a) Alpha particles Name b) Beta particles Charge Mass Greek Symbol c) Gamma particles Equation Symbol Identity ALPHA +2 4 Helium nucleus BETA -1 0(1/2000) Electron GAMMA 0 0 EMR 6. List any three differences between Nuclear and chemical reactions. Chemical Nuclear Bonds are broken and formed Nuclei emits particles and/or rays Atoms are unchanged but rearranged Atoms are sometimes changed into other atoms Involve valence electrons Involves protons, neutrons and electrons Small energy changes Large energy changes Influenced by temp, pressure and other external Not affected by those things factors 7. Which of the three radioactive emissions(alpha, beta , gamma) best fit the following statements? a. These emissions are charged alpha,beta b. This emission is the most massive alpha c. This emission is the most charged alpha d. This emission is the most dangerous outside of the body gamma e. This emission is stopped by thin paper or few centimeters of air alpha f. This emission can travel through fairly thick lead.gamma 8. Which type of radiation-alpha , beta or gamma a. Results in the greatest change in atomic number? Why? Alpha-Changes by 2 b. Results in the least change in atomic number? Why? Gamma-No change in atomic number c. Produces the greatest change in mass number? Why? Alpha-changes mass number by 4 d. Produces the least change in mass number? Why? Beta and Gamma-No change in mass number 9. Complete the following nuclear reaction a. 214 84Po + 2 42He + 2 0-1e ___21888Ra b. 239 93Np → 23994Pu + ___0-1e c. 23592U _____ + 10n → 14256Ba + 9136Kr + 310n d. e. 1 d.27 4 30 13Al + 2He → 15P + _ 0 ___ 235 1 1 139 95 92U + 0n → __2__ 0n + 53I + 39Y n 10. Write nuclear reactions for the following: a. Carbon-14 emits beta particles. d) Thorium-232 goes through alpha decay. b. Radium-226 emits gamma and alpha particles. e) Argon-37 is produced by beta decay. c. Fermium-257 is formed by alpha and gamma emission. 11. Below are the products of decay reactions. Determine the species that decayed. (a) Fm-257 by alpha emission. No-261 (b) Bi-211 by beta emission. Pb-211 (c) Nd-141 by positron emission. Pm-141 (d) Ta-179 by electron capture. W-179 Half Life 12. Gold-191 has a half-life of 12.4 hours. What mass of this isotope would remain after 49.6 hours if you started with a 7.50 mg? 13. The half-life of cesium-137 is 30.2 years. If the initial mass of a sample of cesium-137 is 1.00 kg, how much will remain after 151 years? 0.0313 kg 14. Given that the half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years, consider a sample of fossilized wood that, when alive, would have contained 24 g of carbon-14. It now contains 1.5 g of carbon-14. How old is the sample? 11460 15. What is the half-life of an isotope of plutonium, if the original sample was 10 g and after 420 days there were 1.3 grams left? 16. Palladium -114 has a half-life of 2.4 minutes. What percentage of palladium-114 atoms will remain after the following periods of time? a) 4.8 minutes 7a. 25% b) 4 half-lives 7b. 6.25% c) 6 minutes 7c. 17.7% 17. Once the C-14 activity in a fossil has dropped below 99.8% of it’s original value, it can no longer be accurately measured. What is the age of the oldest fossil we could accurately date using carbon dating? The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. 14 hours 18. What is nuclear fission and how is it used to make useful energy? 19. How do fission reactions differ from fusion reactions? 20. Nuclear fusion powers the Sun. What elements in the Sun are fused together in the Sun? 21. How is the Sun able to produce nuclear fusion? 22. How are radioisotopes used to help humans? 23. List any four applications of nuclear chemistry.