AP Question WS with answers
advertisement

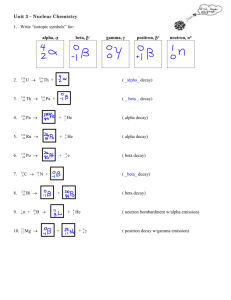
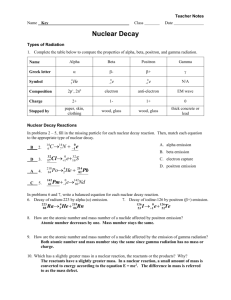
Nuclear AP Worksheet Name_____________________________________ The carbon isotope of mass 12 is stable. The carbon isotopes of mass 11 and mass 14 are unstable. However, the type of radioactivity decay is different for these two isotopes. Carbon-12 is not produced in either case. (a) Identify a type of decay expected for carbon-11 and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that decay process. (b) Identify the type of decay expected for carbon-14 and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that decay process. (c) Gamma rays are observed during the radioactive decay of carbon-11. Why is it unnecessary to include the gamma rays in the radioactive decay equation? (d) Explain how the amount of carbon-14 in a piece of wood can be used to determine when the tree died. Answer: 11 11 0 (a) Positron decay: 6C 5B1 OR 11 0 11 Electron capture: 6C1e 5B 14 14 0 (b) Beta decay: 6C 7N1 (c) Gamma rays have no mass or charge (or they are energy) so they need not be shown in nuclear equations. (d) Measure the amount of C-14 in the dead wood. Compare with the amount of C-14 in a similar living object. Explain each of the following in terms of nuclear models. (a) The mass of an atom of 4He is less than the sum of the masses of 2 protons, 2 neutrons, and 2 electrons. (b) Alpha radiation penetrates a much shorter distance into a piece of material than does beta radiation of the same energy. (c) Products from a nuclear fission of a uranium atom such as 90Sr and 137Ce are highly radioactive and decay by emission of beta particles. (d) Nuclear fusion requires large amounts of energy and to get started, whereas nuclear fission can occur spontaneously, although both processes release energy. Answer: (a) When nucleons are combined in nuclei, some of their mass (mass defect) is converted into energy (binding energy) which is released and stabilizes the nucleus. (b) Alpha particles have a greater mass than beta particles. Thus, their speed (penetrating potential) is less. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is too large and they emit beta particles (converting neutrons into protons) to lower this ratio. (d) Large amounts of energy are needed to initiate fusion reactions in order to overcome the repulsive forces between the positively charged nuclei. Large amounts of energy are not required to cause large unstable nuclei to split apart. 1) Atoms containing radioactive nuclei are called __________. A) radionuclides B) radioisotopes C) nucleons D) nuclides E) radioisophores 2) In what type of radioactive decay does the atomic number of the product increase by one? A) alpha B) beta C) gamma D) positron emission E) electron capture 3) Atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers A) do not exist. B) are isomers. C) are isotopes. D) are allotropes structures. 4) The formation of krypton from rubidium decay is a result of __________. A) alpha emission B) beta emission C) positron emission D) electron capture E) are resonance E) neutron capture 13 5) In the nuclear transmutation, 16 8 O (p, α) 7 N, what is the bombarding particle? A) an alpha particle B) a beta particle C) a gamma photon D) a proton E) a phosphorus nucleus 6) The product of the nuclear reaction in which 28Si is subjected to neutron capture followed by alpha emission is __________. A) 31S B) 33S C) 23Mg D) 25Mg E) 25Al 7) Which one of the following requires a particle accelerator to occur? 59 0 59 1 60 238 1 239 0 A) 59 26 Fe → 27 Co + -1 e B) 27 Co + 0 n → 27 Co C) 92 U + 0 n → 93 Np + -1 e 4 242 1 D) 239 E) none of the above 94 Pu + 2 He → 96 Cm + 0 n 8) Which one of the following is true? A) Some spontaneous nuclear reactions are exothermic. B) Some spontaneous nuclear reactions are endothermic. C) All spontaneous nuclear reactions are exothermic. D) There is no relationship between exothermicity and spontaneity in nuclear reactions. E) All spontaneous nuclear reactions are endothermic. 9) The mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10-24 g. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 × 10-24 g. The mass of the nucleus of an 56Fe atom is 9.289 × 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding energy (in J) for a 56Fe nucleus? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s) A) 2.57 × 10-16 B) 7.72 × 10-8 C) 8.36 × 10-9 D) 7.72 × 10-11 E) 6.07 × 106 10) Which one of the following forms of radiation can penetrate the deepest into body tissue? A) alpha B) beta C) gamma D) positron E) proton 11) Nuclei above the belt of stability can lower their neutron-to-proton ratio by __________. A) beta emission B) gamma emission C) positron emission D) electron capture E) Any of the above processes will lower the neutron-to-proton ratio. 12) The largest number of stable nuclei have an __________ number of protons and an __________ number of neutrons. A) even, even B) odd, odd C) even, odd D) odd, even E) even, equal