Essential Biology G4(HL) - Conservation of Biodiversity
advertisement
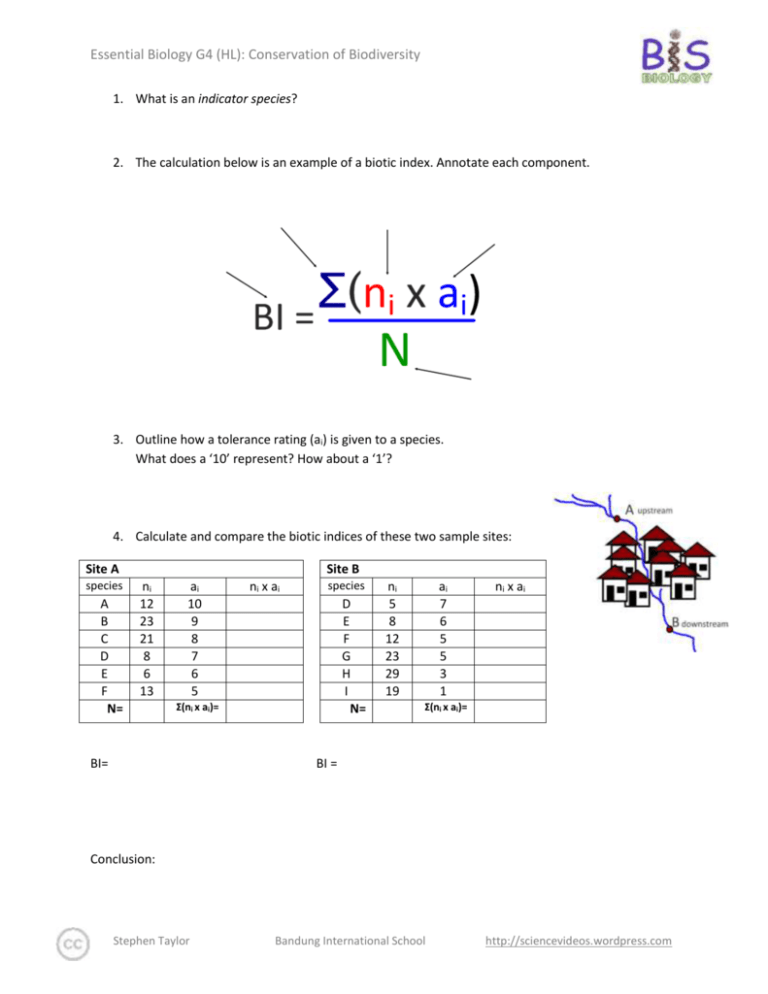
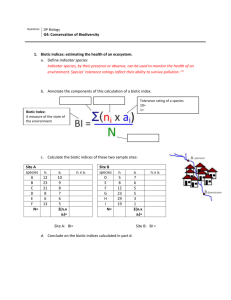
Essential Biology G4 (HL): Conservation of Biodiversity 1. What is an indicator species? 2. The calculation below is an example of a biotic index. Annotate each component. 3. Outline how a tolerance rating (ai) is given to a species. What does a ‘10’ represent? How about a ‘1’? 4. Calculate and compare the biotic indices of these two sample sites: Site A species A B C D E F N= Site B ni 12 23 21 8 6 13 ai 10 9 8 7 6 5 ni x ai species D E F G H I N= Σ(ni x ai)= BI= ni 5 8 12 23 29 19 ai 7 6 5 5 3 1 ni x ai Σ(ni x ai)= BI = Conclusion: Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G4 (HL): Conservation of Biodiversity 5. Define extinction. 6. Outline how a species becomes extinct in terms of evolution. 7. What are some of the anthropogenic causes of species extinction? 8. Outline the factors that contributed to the extinction of one named animal species, due to human impacts. Common name: Linnean name: Habitat: Human impacts: Innate weaknesses: 9. Read the debate on panda extinction here: http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2009/sep/23/panda-extinction-chris-packham What do you think? 10. Although it must not be considered preventative, is reproductive cloning a viable option for conserving endangered species or bringing back extinct species? What are the concerns and difficulties of cloning extinct species? Read more here: http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2009/05/cloned-species/mueller-text Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G4 (HL): Conservation of Biodiversity 11. What is a nature reserve? Give an example in your own country. Use this database to find them: http://www.nationalparks-worldwide.info/ 12. Outline the biogeographical features of nature reserves that promote the conservation of diversity. Use diagrams if needed. Edge Effects Size Habitat corridors 13. What are the dangers of habitat fragmentation? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G4 (HL): Conservation of Biodiversity 14. What is active management with regard to nature reserves? 15. Give some examples of active management strategies and their impacts. 16. What are some of the main ideas of a successful active management strategy? Before beginning: Human interests: Staffing: Legal: Monitoring: Funding: 17. Read this amazing article: http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2008/may/04/conservation.wildlife And watch the talk here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3vfuCPFb8wk How did active management strategies increase diversity in what was a Borneo wasteland? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G4 (HL): Conservation of Biodiversity 18. Distinguish between in-situ and ex-situ conservation measures. 19. Discuss the benefits of both in-situ and ex-situ conservation of plant and animal species, with examples. in-situ (terrestrial and aquatic reserves) ex-situ Advantages Captive breeding: Animal Examples Rehabilitation: Seed banks: Plant examples Botanic gardens: 20. Visit the CITES database and look for endangered species in your area: http://www.cites.org/eng/resources/species.html Use it to practice your classification and taxonomy and to find out about factors causing problems and the status of local species. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
![20-%20Conservation%20of%20Biodiversity[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007169774_1-d8aa5010241d91dc01f2a30f36c56059-300x300.png)