File
advertisement

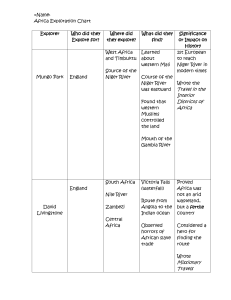
Source Analysis Criterion D: Thinking Critically Year 1 G7 Task: You are going to be looking at multiple sources. You will need to analyze them and complete the tasks. Nature Origin and Purpose (NOP) 1. Outline the Nature, origin and purpose. Source Nature/Origin What is it? Who created it? When? Where? Primary or secondary source? Purpose Why was it made? Who was it made for (Audience)? A B C Source Analysis Written Text: Reading for Information I. Read the text through to the end. II. Go back and highlight the key points. Source A: an excerpt from the Historychannel.com Website The Gift of the Nile The River Nile, at 6695 km (sources vary), is the longest river in the world. Egypt is often referred to as the Gift of the Nile. The Nile was very important to Ancient Egyptians. With its annual flood the Nile provided most of the water used to grow crops in Egypt, whereas the rest of Egypt is a desert. Indeed, it is hard to imagine Egypt existing at Source Analysis Criterion D: Thinking Critically Year 1 G7 all without the great river. Heavy rains and melting snow in the mountains of Ethiopia feed the tributaries which form the White Nile and the Blue Nile, before joining to become the great river. The torrent pours into Egypt causing the Nile to overspill its banks. When the waters eventually recede they leave behind a rich black soil which Ancient Egyptians referred to as the Black Land (fertile soil). Question 1. What are the most important points we can learn from Source A about Answer with quotes from the source the source. Try to write two answers each with a quote. There are two main points of source A. First, we can learn that … For example (add quote here). An additional main point is…, for example (add quote here). ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Source Analysis Graphs, Charts: Observation I. Study the source for 1-2 minutes. Form an overall impression of the source and then examine individual items. II. Use the chart below to help you analyze the chart. Source Analysis Criterion D: Thinking Critically Year 1 G7 Water Volume of the Nile Rivers Source E: a graph from wikipedia.org Source B Graph or Chart Analyzing structure Analyzing Information/data Title: Highest Point: What is the horizontal axis (numbers on the bottom): Lowest Point: Vertical axis (Numbers on the side): Do the numbers trend up or down or up and down? Overall do the numbers trend up or down or the same? Q2. What can we learn about rainfall (precipitation) in Egypt from Source B? *Give two clear answers to the question and include data or descriptions from the source. Include trends, high and low points. The most important thing we can learn from source B is… for example, we can see (description or data here). Additionally, we can learn…, as evidenced by (add description or data here). ____________________________________________________ Source Analysis Criterion D: Thinking Critically Year 1 G7 ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Question 3. Compare: Does Source B agree with Source A and C? Source C Side by side photos from Historychannel.com Figure 2. When the flood water is gone rich earth is left for farming. Figure 1. The Nile during the flood season. Source A says Source B shows Source C shows