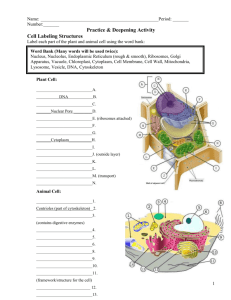
Cell Organelles

Cell Organelles
1.
Nucleus a.
Control center b.
Holds information and instructions c.
Surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double membrane) which contains tiny openings (pores) which allow materials to move out of nucleus d.
Contains nucleolus which is a dark area that manufactures rRNA to make ribosomes e.
Holds DNA – genetic info in long thin threads wrapped around histone proteins (chromatin) f.
Chromatin coils into chromosomes for cell division g.
Found only in eukaryotic cells
2.
Plasma Membrane a.
Phospholipid bilayer – fluid mosaic b.
Outer boundary of cell – all cells have one c.
Contains proteins
1) Integral – penetrate bilayer
2) Peripheral – attached to surface
3) Channel, carrier, receptor ,recognition, enzymatic, transmembrane d.
Semi-permeable –controls what goes in and out of cell e.
Contains cholesterol – prevents freezing f.
Passive and active transport g.
Glycoproteins and glycolipids
3.
Ribosomes a.
Found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells b.
Make proteins (protein synthesis site) c.
Tiny d.
2 subunits (large and small) e.
Read mRNA f.
Free (in cytoplasm) g.
Bound (attached to rough ER
4.
Endoplasmic Reticulum a.
Membrane structure only in eukaryotic cells b.
Transports materials c.
Site of manufacturing materials d.
Rough (studded w/ ribosomes) e.
Smooth f.
Attached to nuclear envelope g.
Smooth and rough are continuous with each other h.
Materials travel through and reach the end where they are packaged in a ER membrane bubble (vesicle)
5.
Golgi Complex a.
only in eukaryotic cells b.
flattened sacs c.
vesicles from ER join with it and empty contents inside d.
materials are modified and packages for secretion e.
materials leave opposite side via vesicles that can fuse with plasma membrane and release contents out of cell, or can become vacuoles or lysosomes
6.
Vacuole a.
Only in eukaryotic cells b.
Storage sac c.
Large, central vacuole in plants holds water and puts pressure on cell wall to give plants support d.
Contractile vacuole in single celled organisms pumps water out of cell so it won’t explode
7.
Lysosome a.
Only in eukaryotic cells b.
Membrane pocket filled with hydrolytic enzymes c.
Forms from Golgi d.
Digests food,waste and old organelles e.
Mostly in animal cells
8.
Mitochondria a.
Only in eukaryotic cells b.
Double membrane c.
Inner membrane is folded (cristae) d.
Liquid inside = matrix e.
Cellular respiration f.
Enzymes in cristae g.
Produce ATP from sugar h.
Powerhouse of cell i.
Contains own DNA and ribosomes j.
Sugar + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
9.
Chloroplasts a.
Only in eukaryotic plant and algae cells b.
Double membrane c.
Contains own DNA & ribosomes d.
Inner membrane in disc-like structures = thylakoids e.
Thylakoids are stacked = grana f.
Liquid inside = stroma g.
Contain green pigment (chlorophyll) h.
Photosynthesis i.
Carbon dioxide + water + light = sugar + oxygen
10.
Plastids
a.
Only in plant cells b.
various functions c.
chloroplasts (see above) d.
leucoplasts (store starch) e.
chromoplasts (contain pigments other than green)
11.
Peroxisomes a.
Contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen to oxygen making hydrogen peroxide which is then broken down to water
12.
Cytoskeleton a.
Made of proteins
1) Microfilaments (made of actin; smallest)
2) Intermediate filaments
3) Microtubules (made of tubulin; hollow tubes; largest) b.
Support, shape, motility, anchor spot for organelles, track for organelle movement
13.
Centrioles a.
Microtubule-based structures b.
Found only in animal cells c.
Found in pairs d.
Located in centrosome area near nucleus e.
Helps organize cytoskeleton during cell division
14.
Cilia & Flagella a.
Microtubule structures attached to outside of cell b.
Provide movement for cell c.
Cilia = short, humdreds or more on cell surface d.
Flagella = long, only one or two
15.
Cell Wall a.
Only in plant cells, fungal cells, some prokaryotes and some protists b.
Made of cellulose in plant cells c.
Made of chitin in fungal cells d.
Primary cell wall e.
Secondary cell wall (between primary and plasma membrane) f.
Middle lamella (made of pectin) – between cells g.
Rigid support for cell h.
Works with central vacuole in plant cells to hold plant up