Chapter 1 The Legacy of the Roman Empire
advertisement

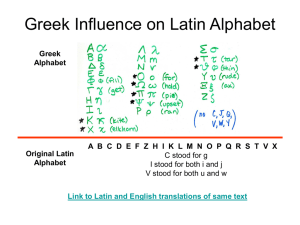
Chapter 1 The Legacy of the Roman Empire IV. The Legacy of Roman Architecture and Engineering (1.4) The Romans borrowed ideas from the Greeks and improved on these ideas in ways that future engineer and architects would imitate. A. Architecture 1. arch –used for a ceiling or to support a ceiling or roof. 2.vault-is an arch used for a ceiling or to support a ceiling or roof. 3. dome-is a vault in the shape of a half circle that rests on a circular wall. 4. Concrete-Romans used concrete to help them build much bigger arches than anyone attempted before. (Mixture of broken stone, sand, cement and water and allowing mixure to harden). B. Examples of structures 1. Pantheon- a magnificent temple that still stand in Rome, is famous for its huge dome. 2. Stadium 3. Triumphal arch-huge monument built to celebrate great victories or achievements. C. Engineering Greatest builders or ROADS, BRIDGES and AQUEDUCTS 1. Aqueduct-a pipe or raised channel built to carry water over a long distance. 2. Roads-build with layers of stone, sand and gravel. Their techniques set the standard of road building for 2,000 years. I. The Legacy of Roman Language and Writing (1.5) Important legacy of Rome for people in medieval times was the Romans’ language, LATIN. A. Latin 1. After the fall of the empire, Latin continued to be used by scholars and the Roman Catholic Church. a. Scribes-used Latin to create important documents. b. Educated European nobles learned Latin so they could communicate with their peers in other countries. c. Several modern European languages developed from Latin; i. Italian V. ii. Spanish iii. French d. We still use the Latin alphabet, (although Latin had 23 letters and English has 26). e. Names of several months come from Latin. f. Proverbs-a popular saying meant to express something wise or true. i. Latin proverbs are still in use (example: reverse side of penny-E pluribus unum-“out of many, one” The Legacy of Roman Philosophy, Law and Citizenship (1.6) Roman philosophy, law and ideas about citizenship were greatly influenced by the Greeks. But Romans mad contributions of their own that they passed on to future generations. A. Stoicism- Stoics believed that a divine (godly) intelligence ruled all of nature. 1. Many upper class Romans adopted this philosophy and made it their own. 2. To the Stoics, the one truly good thing in life was to have a good character. 3. Self-Control and courage B. Law and Justice1. Marriages 2. Inheritances 3. Contracts (agreements) between people, as well as countless other areas of daily life. 4. Justice a. Natural Law-every person had rights. (echoed in our Declaration of Independence) b. Judges in Roman courts tried to make just, or fair, decisions that respected people’s rights. C. Citizenship 1. Originally people had to be a citizen of the city-state of Rome. a. overtime, Rome’s leaders gradually extended citizenship to all free people in the empire. VI. Chapter Summary A. Art, 1. sculpture 2. mosaics 3. glass B. Architecture1. arches 2. domes 3. vaults C. Engineering1.construction, methods and standards lasted thousands of years. D. Language and Writing1. Many words and word parts in modern languages 2. Roman numerals appear today E. Philosophy, Law and Citizenship1. Stoicism 2. rule of law and justice shaped law codes and government structures of many nations today.