rock lesson plan
advertisement

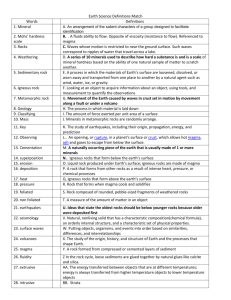
Important Rock Concepts and Vocabulary Igneous Rocks- All rocks on Earth were initially igneous in nature. Igneous rocks form as liquid magma cools, forming crystal structured rocks. There are many different types of igneous rocks. Metamorphic Rocks- Metamorphic rocks form deep within the Earth when heat and pressure are applied to either igneous rocks or sedimentary rocks. This heat and pressure in essence cooks the rocks, changing their structure substantially metamorphic rocks form deep within the Earth when heat and pressure are applied to either igneous rocks or sedimentary rocks. This heat and pressure in essence cooks the rocks, changing their structure substantially. The rocks are partially melted and the chemicals within them are rearranged so that the final rock is very different than the original rock. The final state of a metamorphic rock depends on the amount of pressure the rock was subjected to, the amount of heat the rock was subjected to, and the amount of time the rock was subjected to pressure and heat. One very common metamorphic rock is marble. Marble is formed when heat and pressure are applied to limestone for many thousands of years. Sedimentary Rocks- Over the course of millions of years, the igneous rocks are weathered down by forces of wind and water. Fine particles of dirt begin to cover the landscape. Often, these small rock particles end up being suspended in water, and find their way to the bottom of lakes, streams, and the ocean. Slowly, the layer of sediment on the bottom of lakes, and especially on the bottom of the ocean grows deeper and deeper, reaching depths of thousands of feet. The weight of all the sediment becomes immense, pushing down on lower layers of sediment with tremendous force. In addition, a number of minerals, which act like cement, bond the sediment together, causing it to form sedimentary rock. Lava & Magma- Molten, or hot liquefied, rock located deep below the Earth's surface is called magma. Magma is formed when temperatures within Earth's crust or mantle are very hot and when pressure in places within those layers decreases Rock Cycle- There are three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Each of these types of rocks are formed in different ways and each type of rock can be changed into each of the other types of rock. Geologists call this process the Rock Cycle. Essentially the rock cycle is the process that makes and recycles rocks. Weathering- Weathering takes place as rocks are broken down into progressively smaller pieces by the effects of weather. These pieces do not move to a new location, they simply break down, but remain next to one another. Erosion- The carrying away of sediments Lesson Plan Format Name: Alex Sargent Subject: Rocks & the Rock Cycle Lesson Title: Igneous Rocks Virginia SOL: 5.7a Start time: Grade: 5th Stop time: Date: 2/13/15 Objectives (What do you want students to know, do, or feel as a result of your instruction?) 1. TSW identify what an igneous rock is 2. TSW identify and understand the characteristics of igneous rocks 3. Igneous rocks, magma Critical vocabulary: Study jam, rock notes Materials/resources: Pre-assessment: (How will you know if your students already know what you are teaching?) Intro (how do you capture their attention and get them interested?): Study Jams Video on Igneous Rocks http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/science/rocks-minerals-landforms/igneous-rocks.htm Body (what comes after your interesting intro?) Go through Igneous Rocks power point and take notes on characteristics and examples. Go over Igneous rocks through an interactive rock cycle. Look at a sample of an Igneous rock and identify its Igneous characteristics Closure (purposeful summary-help them remember today or anticipate tomorrow): Homework: Assessment: (How will you assess if they have mastered your objectives? Be specific.) Quick Assessment Exit Slip: name 2 characteristics of Igneous Rocks and name one example. Are you differentiating lesson content, process, or product by readiness, interest, or learning profile? Explain below. For cooperative learning explain how you have insured: positive interdependenceindividual accountabilitygroup processingsocial skillsface-to-face interaction-