Exam Outline
advertisement
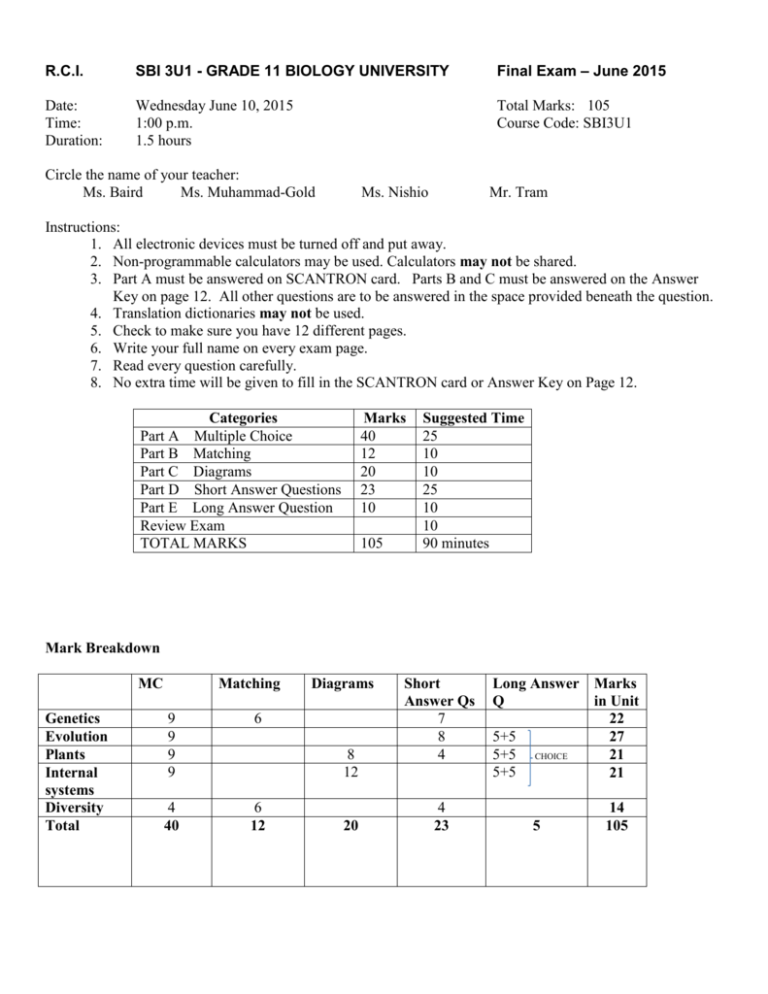
R.C.I. SBI 3U1 - GRADE 11 BIOLOGY UNIVERSITY Final Exam – June 2015 Date: Time: Duration: Wednesday June 10, 2015 1:00 p.m. 1.5 hours Total Marks: 105 Course Code: SBI3U1 Circle the name of your teacher: Ms. Baird Ms. Muhammad-Gold Ms. Nishio Mr. Tram Instructions: 1. All electronic devices must be turned off and put away. 2. Non-programmable calculators may be used. Calculators may not be shared. 3. Part A must be answered on SCANTRON card. Parts B and C must be answered on the Answer Key on page 12. All other questions are to be answered in the space provided beneath the question. 4. Translation dictionaries may not be used. 5. Check to make sure you have 12 different pages. 6. Write your full name on every exam page. 7. Read every question carefully. 8. No extra time will be given to fill in the SCANTRON card or Answer Key on Page 12. Categories Part A Multiple Choice Part B Matching Part C Diagrams Part D Short Answer Questions Part E Long Answer Question Review Exam TOTAL MARKS Marks 40 12 20 23 10 105 Suggested Time 25 10 10 25 10 10 90 minutes Mark Breakdown MC Genetics Evolution Plants Internal systems Diversity Total Matching 9 9 9 9 6 4 40 6 12 Diagrams 8 12 20 Short Answer Qs 7 8 4 4 23 Long Answer Marks Q in Unit 22 5+5 27 5+5 CHOICE 21 5+5 21 5 14 105 UNIT 1: GENETICS Cell Cycle: interphase, mitosis or meiosis, cytokinesis Steps of mitosis vs. steps of meiosis (prophase I and II, anaphase I and II, metaphase I and II, telophase I and II) Genetic variation: independent assortment, crossing over Karyotype Phenotype vs. genotype Genetic disorders e.g. Trisomy 21 Body cell, gametes Diploid, haploid, n, 2n Chromatin, chromosomes, homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, tetrad DNA structure and function Complementary base pairing Mendelian and Non-Mendelian genetics o recessive trait, dominant trait, phenotype, genotype, homozygous, heterozygous, allele, gene o monohybrid cross, dihybrid cross, sex-linkage o incomplete dominance and codominance, multiple alleles UNIT 2: EVOLUTION Evolutionary theory Darwin’s theory of natural selection Lamarck’s theory of acquired characteristics Types of mutations Adaptation and Examples of Adaptation; Adaptive radiation Natural Selection vs. Artificial selection Evidence for evolution: artificial selection (selective breeding), biogeography, fossil record, comparative anatomy (homologous, analogous, vestigal structures), divergent, convergent, parallel evolution, genetic evidence (DNA, amino acids), industrial melanism, embryology Hardy-Weinberg principle Factors/Mechanisms that cause evolution/speciation: genetic drift (founder effect, bottleneck effect), gene flow, non-random mating, mutations, natural selection Patterns of selection from selective pressures: stabilizing, directional, disruptive Barriers to reproductions/Mechanisms of speciation: allopatric speciation, sympatric speciation Prezygotic reproductive isolating mechanisms: ecological, behavioral, temporal, mechanical, gamete Postzygotic isolating mechanisms: reduced hybrid viability, reduced hybrid fertility, hybrid breakdown UNIT 3: INTERNAL SYSTEMS Mechanical digestion, chemical digestion Structure and function and location of the digestive system: all salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, epiglottis, stomach, pyloric and cardiac sphincter, gall bladder, liver, small intestine( all 3 parts), large intestine, rectum, pancreas, peristalsis, bolus, chyme, gastric juice, pancreatic juice, bile Molecules (e.g. bile, bicarbonate, pepsinogen, lipase) used to digest/breakdown proteins, carbohydrates and lipids Structure and function of circulatory system: pulmonary and systemic system, label parts of the heart, pathway of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flow Structure and function of respiratory system: nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, capillaries, alveoli, diaphragm UNIT 4: PLANTS Process of germination (radicle, hypocotyl, plumule, colyledon, micropyle) Characteristics and examples of major types angiosperms Structure and function of: flower, roots, stems and leaves Monocots vs. dicots Structure and function of - Vascular tissue: xylem, phloem, vascular bundles - Dermal tissue: epidermis, cuticle, stomata, guard cells -Meristematic tissue: vascular and cork cambium, primary vs. secondary growth -Ground tissue: sclerenchyma, collenchyma, parenchyma Word equation of cellular respiration and photosynthesis Structure and Function (cross section) of: -monocot stem, herbaceous dicot stem, woody stem, leaf, root Formation of wood Describe how water and minerals move from soil to the leaves using root pressure, capillary action and transpirations, and explain the role of active transport, osmosis, the Casparian strip, cohesion, adhesion, guard cells, and stomata in these processes Water transport: bulk flow, root pressure, adhesion and cohesion, transpiration UNIT 5: DIVERSITY OF LIVING THINGS Taxonomic levels: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species Binomial nomenclature & writing scientific names, e.g. Homo sapiens or Homo Sapiens Characteristics and examples of organisms in all six kingdoms (chart) Making a dichotomous key