Biology OneGuided Notes PacketChapter 16 Population Genetics
advertisement
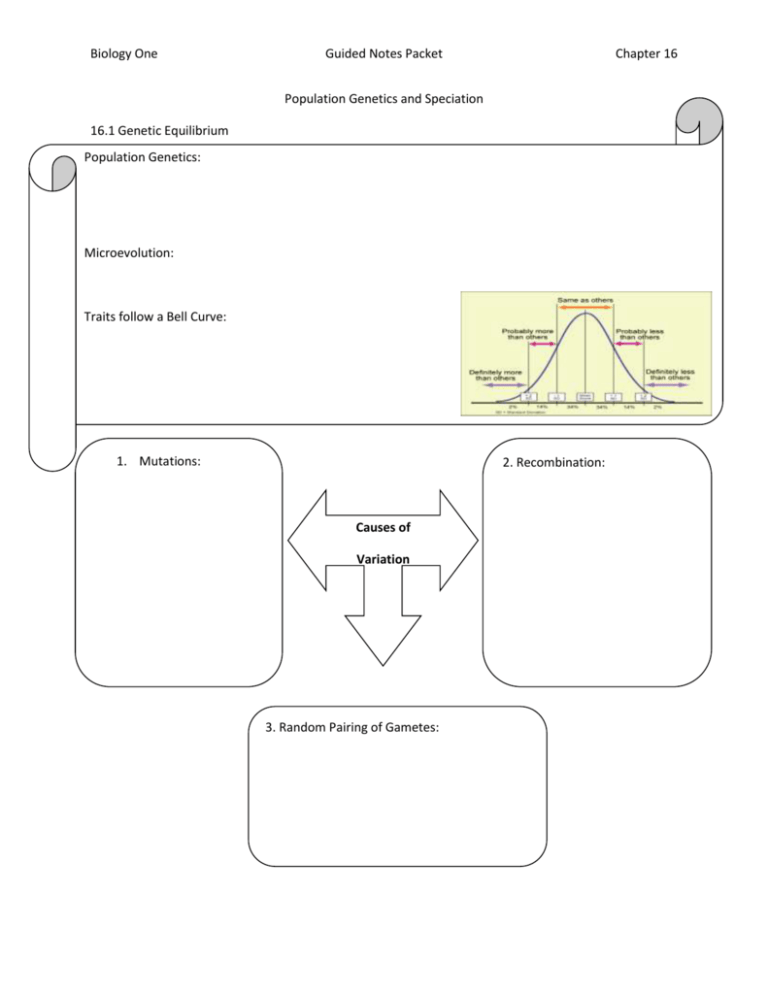
Biology One Guided Notes Packet Chapter 16 Population Genetics and Speciation 16.1 Genetic Equilibrium Population Genetics: Microevolution: Traits follow a Bell Curve: 1. Mutations: 2. Recombination: Causes of Variation 3. Random Pairing of Gametes: Biology One Guided Notes Packet Chapter 16 Understanding Evolution through Genetics ---- Key Terms Gene Pool: Allele Frequency: Calculated by: Example: Phenotype Frequency: Calculated by: Example: Hardy-Weinberg Genetic Equilibrium: Ideal Situation (Hypothetical) for a Population would be NO CHANGE OVER TIME (meaning there is no evolution) 5 Criteria for the IDEAL situation: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Is this Possible? Biology One Guided Notes Packet Chapter 16 16.2 Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium A Disruption in Any One or Combination of the 5 criteria will result in change over time (EVOLUTION) of the species! 1. Mutation: 2. Gene Flow: 3. Genetic Drift: 4. Nonrandom Mating: 5. Natural Selection: Biology One Guided Notes Packet Chapter 16 1. Disruptive: 2. Directional: 3. Stabilizing: Types of Natural Selection 16.3 Formation of Species Key Terms: Speciation: Morphology: Species: Methods to Determine Species - - - - - 2 Competing Concepts: Morph = Bio = Biology One Guided Notes Packet Geographic Isolation: Reproductive Isolation: Rates of Speciation: 1. Gradualism: 2. Punctuated Equilibrium: Chapter 16