File
advertisement
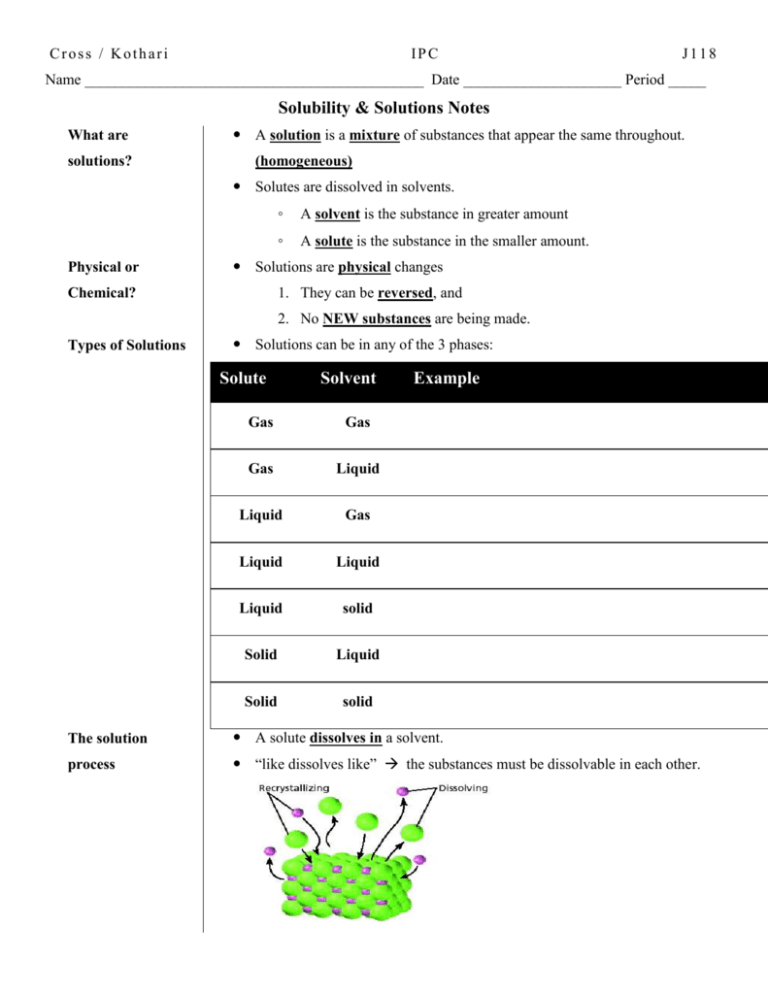
Cross / Kothari IPC J118 Name _____________________________________________ Date _____________________ Period _____ Solubility & Solutions Notes What are solutions? A solution is a mixture of substances that appear the same throughout. (homogeneous) Solutes are dissolved in solvents. Physical or ◦ A solvent is the substance in greater amount ◦ A solute is the substance in the smaller amount. Solutions are physical changes 1. They can be reversed, and Chemical? 2. No NEW substances are being made. Types of Solutions Solutions can be in any of the 3 phases: Solute Solvent Gas Gas Gas Liquid Liquid Gas Liquid Liquid Liquid solid Solid Liquid Solid solid Example The solution A solute dissolves in a solvent. process “like dissolves like” the substances must be dissolvable in each other. Dissolvable The amount of a substance that can be dissolved in a solvent is called solubility. What is solubility Solubility depends on the nature of the substances both solvent and solute. Solubility of substances can be compared by measuring. Solubility is the mass of solute that can be dissolved in 100g of water under a given set of conditions (temperature and pressure). Solubility Rules “Like dissolves Like” This means, ionic compounds will dissolve other ionic compounds. Polar substances (partially charged covalent compounds) dissolve other polar substances. Water Nonpolar substances dissolve other nonpolar susbsances. Water is known as the Universal Solvent This is because it is POLAR How to Change Increase Solubility Stirring Solid into liquid Gas into liquid Grinding Heating Pressure How solutes effect All solute particles – affect the physical properties of the solvents solvents Adding solutes lowers the freezing point of the solvent Adding solutes raises the boiling point of the solvent Cross / Kothari IPC J118 Name _____________________________________________ Date _____________________ Period _____ Solubility & Solutions Notes What are solutions? A ___________________ is a _____________________ of substances that appear the same throughout. ___________________________ Solutes are dissolved in solvents. Physical or ◦ A _________________ is the substance in greater amount ◦ A _________________ is the substance in the smaller amount. Solutions are ____________________ changes 1. They can be _________________________, and Chemical? 2. No _______________________________are being made. Types of Solutions Solutions can be in any of the 3 phases: Solute Solvent Gas Gas Gas Liquid Liquid Gas Liquid Liquid Liquid solid Solid Liquid Solid solid Example The solution A solute ______________________ a solvent. process “like dissolves like” the substances must be dissolvable in each other. Dissolvable The _______________________________________________________ ___________________________ in a solvent is called solubility. What is solubility Solubility ______________ the nature of the substances _______________ __________________________________________ Solubility of substances can be compared by measuring. Solubility is the ______________________ that can be _____________________ in ______________________________ under a given set of conditions (temperature and pressure). Solubility Rules “Like dissolves Like” This means, ionic compounds will _________________________________ ____________________________ Polar substances (partially charged covalent compounds) _______________ _________________________________________ Water Nonpolar substances ___________________________________________ Water is known as the ____________________________________ This is because it is __________________ How to Change Increase Solubility Stirring Solid into liquid Gas into liquid Grinding Heating Pressure How solutes effect All solute particles – affect the ____________________________________ solvents ______________________________________________ point of the solvent ____________________________________________ point of the solvent