Science
advertisement
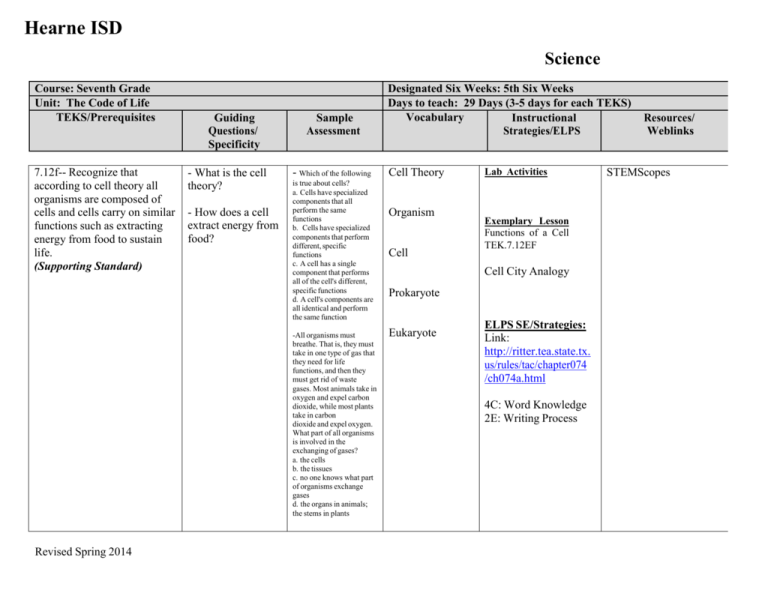
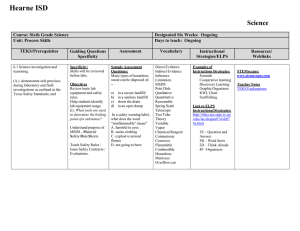
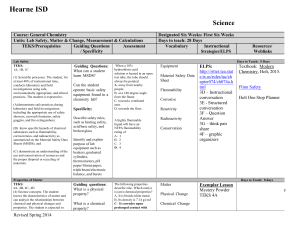
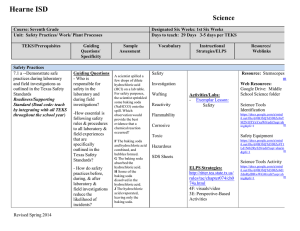
Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.12f-- Recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life. (Supporting Standard) Guiding Questions/ Specificity - What is the cell theory? - How does a cell extract energy from food? Sample Assessment - Which of the following is true about cells? a. Cells have specialized components that all perform the same functions b. Cells have specialized components that perform different, specific functions c. A cell has a single component that performs all of the cell's different, specific functions d. A cell's components are all identical and perform the same function -All organisms must breathe. That is, they must take in one type of gas that they need for life functions, and then they must get rid of waste gases. Most animals take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide, while most plants take in carbon dioxide and expel oxygen. What part of all organisms is involved in the exchanging of gases? a. the cells b. the tissues c. no one knows what part of organisms exchange gases d. the organs in animals; the stems in plants Revised Spring 2014 Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Cell Theory Organism Cell Lab Activities Exemplary Lesson Functions of a Cell TEK.7.12EF Cell City Analogy Prokaryote Eukaryote ELPS SE/Strategies: Link: http://ritter.tea.state.tx. us/rules/tac/chapter074 /ch074a.html 4C: Word Knowledge 2E: Writing Process Resources/ Weblinks STEMScopes Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.12d-- Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole (Supporting Standard) Guiding Questions/ Specificity - What structures and functions differentiate plant from animal cells? Sample Assessment - A cell's membrane is composed of two layers of lipid molecules. What is the main function of a cell membrane? a. control what enters and exits the cell b. construct long chains of amino acids c. direct the functions of the cell's organelles d. stores energy for later use - Which of the following organelles is most important in providing energy to a cell? a. cell membrane b. vacuole c. mitochondrion d. nucleus Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Organelle Cell membrane Cell wall Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Microscope Lab Exemplar Lesson TEK7.12D Structures and Functions Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondrion - Chloroplast Cell Venn Diagram Cell Model Microscope Care and Use Cells and Their Organelles Cell World Student Project ELPS Strategies: Vacuole http://ritter.tea.state.tx. us/rules/tac/chapter074 /ch074a.html 4C: Word Knowledge 2E: Writing Process Revised Spring 2014 Resources/ Weblinks Structure and Function http://www.cellsalive.com cells/cell_model.htm Comparing Plant and Animal Cells – Microsco Lab http://www.nclark.net/An p lantCells.htm Inside of a Cell http://learn.genetics.utah.e du/content/cells/insideace / Functions of Cells Diagram http://teach.genetics.utah. du/content/begin/cells/pri /InsideaCellWorksheet.pd Stemscopes: http://mansfieldisd.stemsc pes.com/login Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.12e-- Compare and describe the functions of a cell to the functions of organisms such as waste removal. Guiding Questions/ Specificity Sample Assessment - How do they ways plant cells and animal cells reproduce, get rid of waste, grow, and obtain energy compared to one another? Most animals take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide, while most plants take in carbon dioxide and expel oxygen. What part of all organisms is involved in the exchanging of gases? a. the tissues b. the organs in animals; the stems in plants c. No one knows what part of organisms exchanges gases. d. the cells - All cells need energy to perform various processes and to make molecules that are necessary to sustain their lives. From where do cells primarily get this energy? a. mitosis b. heat c. food d. water Revised Spring 2014 Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Cell Organism Exemplar Lesson. TEK7.12EF Structure and Function Waste removal - Excretion Metabolism Cell City Analogy Function of Cells Diagram Resources/ Weblinks Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.14a-- define heredity as the passage of genetic instruction from one generation to the next generation Guiding Questions/ Specificity Sample Assessment - What are genes and how are they inherited? Teacher Notes: Emphasize the relevance of scientist contribution (7.3d) of Gregor Mendel -Using the Punnett square above, choose the probability that the recessive trait will emerge a. 100% b. 75% c. 25% d. 0% -An offspring’s Punnett square is shown above. The mother is known to have two recessive genes for brown eyes. What is the father’s genotype for brown eyes? a. BB b. Bb c. bb d. bB Revised Spring 2014 Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Heredity Genetics Gene Generation Descendant Ancestor Dominant Recessive Punnett Square Homozygous Heterozygous Purebred Genotype Phenotype Variation Mutation Resources/ Weblinks Lab Activities - Genetics with a Smile Family Traits and Traditions http://teach.genetics.utah. du/content/begin/traits/fa m ilytraitsandtraditions.pdf Exemplar Lesson TEK7.14A Heredity 7.14C Inherited Traits Google Drive: Middle School Science - Baby Lab Genetics Scavenger Hunt Family Traits and Traditions ELPS SE/Strategies: Link: http://ritter.tea.state.tx. us/rules/tac/chapter074 /ch074a.html 4F: visuals 3J: manipulatives 2H: comprehension strategies Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.14b-- compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring from sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction (Supporting Standard) Revised Spring 2014 Guiding Questions/ Specificity Sample Assessment -What are the differences between offspring in sexual and asexual reproduction? -How do the offspring of asexual reproduction differ from those of sexual reproduction? A. Cells produced through asexual reproduction are genetically identical to their parents. B. Cells produced through asexual reproduction do not grow and divide. C. Cells produced through asexual reproduction do not posses genetic material. D. Cells produced through asexual reproduction have a unique set of genetic instructions unlike their parents. Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Asexual reproduction Sexual Reproduction Offspring Exemplar Lesson TEK7.14B AsexualSexual Reproduction Investigating Reproductive Strategies Activity ELPS SE/Strategies: Link: http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/rul es/tac/chapter074/ch074a.ht ml 4E: Graphic Organizer 2H: comprehension strategies Resources/ Weblinks Investigating Reproductiv Strategies Activity http://teach.genetics.utah. du/content/begin/traits/Re roductiveStrategies.pdf Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.14c-- recognize that inherited traits of individuals are governed in the genetic material found in the genes within chromosomes (Supporting Standard) Guiding Questions/ Specificity - Where are genes located? - Where do inherited traits come from? Sample Assessment -Which of the following determines the genetic traits of an organism? a. acquired characteristics b. inherited material from the mother c. inherited material from the father d. inherited material from both the mother and the father -If an organism reproduces asexually, its offspring will most likely be a. genetically identical to the parent b. genetically different from each other c. produced as a result of fertilization d. produced from specialized cells known as gametes Revised Spring 2014 Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Trait Genetic material DNA Gene Chromosomes Physical traits Exemplar Lesson Levels of Organization TEK7.14C - DNA Extraction Lab Dominant and Recessive Traits Lab ELPS SE/Strategies: Link: http://ritter.tea.state.tx. us/rules/tac/chapter074 /ch074a.html 4C: Word Knowledge 2E: Writing Process Resources/ Weblinks DNA Extraction Lab http://learn.genetics.utah.e du/content/labs/extraction howto/ Reference to Inherited Traits http://teach.genetics.utah. du/content/begin/traits/tra sreference.pdf Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.12c-- Recognize the levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. Guiding Questions/ Specificity Sample Assessment - What are the levels of organization in plants and animals? -The level of organization of living things is cells, tissues, organs, and a. systems b. ecosystems c. functions d. organelles Teacher Notes Plant cells were covered in the first six weeks. Review briefly to compare to animal cells. Revised Spring 2014 -What are the most basic building blocks of all organisms? a. cells b. blood c. tissue d. organs Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Cell Tissue Organ Organ system Organism - Levels of Organization Activity ELPS SE/Strategies: Link: http://ritter.tea.state.tx. us/rules/tac/chapter074 /ch074a.html 4C: Word Knowledge 2E: Writing Process Resources/ Weblinks Hearne ISD Science Course: Seventh Grade Unit: The Code of Life TEKS/Prerequisites 7.12b--identify the main functions of the systems of the human organism, including the circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, muscular, digestive, excretory, reproductive, integumentary, nervous and endocrine systems. (Supporting Standard) Revised Spring 2014 Guiding Questions/ Specificity Guiding Question: What are the primary functions of the human body systems? Teacher Note: - From this unit students should gain an understanding of what type of work each system performs, not just the anatomical names of the systems, organs, and parts. Sample Assessment Two systems that work closely to maintain overall homeostasis in the body are the _ A. circulatory and endocrine B. respiratory and excretory C. excretory and endocrine D. nervous and endocrine Answer. D Designated Six Weeks: 5th Six Weeks Days to teach: 29 Days (3-5 days for each TEKS) Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Function System Human organism Circulatory system Respiratory system Skeletal system Muscular system Digestive system Excretory system Reproductive system Integumentary system Nervous system Endocrine system Required Lab: Earth worm dissection Resources/ Weblinks Virtual Worm Dissection http://www.naturewatch.ca/eng sh/wormwatch/virtual_worm/in ex.html Other Suggested Activities: Heart Beat Lab Order of the Digestive System Human Body Systems Review Life Process Notes and Body Systems Bones, Bones, Everywhere Lab - Muscle Action Lab Virtual Frog Dissection http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/g nbio/virtual_labs/BL_16/BL_1 html