Microsoft Word - Chem.1st.Six.Wks.14.15

Hearne ISD
Science
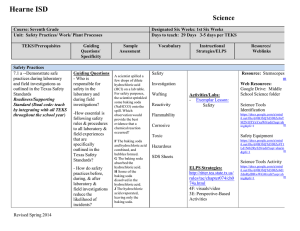
Course: General Chemistry
Units: Lab Safety, Matter & Change, Measurement & Calculations
TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions
/ Specificity
Assessment
Lab Safety
TEKS:
1A, 1B, 1C
(1) Scientific processes. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts laboratory and field investigations using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. The student is expected to.
(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations, including the appropriate use of safety showers, eyewash fountains, safety goggles, and fire extinguishers;
(B) know specific hazards of chemical substances such as flammability, corrosiveness, and radioactivity as summarized on the Material Safety Data
Sheets (MSDS); and
(C) demonstrate an understanding of the use and conservation of resources and the proper disposal or recycling of materials.
Properties of Matter
TEKS:
4A, 4B, 4C, 4D
(4) Science concepts. The student knows the characteristics of matter and can analyze the relationships between chemical and physical changes and properties. The student is expected to:
Guiding Questions:
What can a student learn MSDS?
Can the student operate basic safety equipment found in a chemistry lab?
Specificity:
Describe safety rules, such as heating safety, acid/base safety, and broken glass
Identify and explain purpose of lab equipment such as beakers, graduated cylinders, thermometers, pH paper/litmus paper, triple beam/electronic balance, and burets
Guiding questions:
What is a physical property?
What is a chemical property?
When a 10% hydrochloric acid solution is heated in an open test tube, the tube should always be pointed
A . away from nearby people.
B.
at a 180 degree angle from the flame.
C.
toward a ventilated area.
D.
towards the floor.
A highly flammable liquid will have an
NFPA flammability rating of
A.
1
B.
2
C.
3
D . 4
The following properties describe zinc. Which one(s) is (are) chemical properties?
A.
It is bluish-white metal.
B.
Its density is 7.14 g/cm3
C . It corrodes upon prolonged contact with
Revised Spring 2014
Designated Six Weeks: First Six Weeks
Days to teach: 28 Days
Vocabulary
Matter
Physical Change
Chemical Change
Instructional
Strategies/ELPS
Equipment
Material Safety Data
Sheet
Flammability
Corrosive
Reactivity
Radioactivity
Conservation
ELPS: http://ritter.tea.stat e.tx.us/rules/tac/ch apter074/ch074a.h tml
3D – Instructional conversation
3E - Structured conversation
3F – Question
Answer
3G – think pair share
4F – graphic organizers
Days to Teach: 5 Days
Textbook: Modern
Chemistry, Holt, 2015.
Flinn Safety
Holt One Stop Planner
Exemplar Lesson
Mystery Powder
TEKS 4A
Resources/
Weblinks
Days to Teach: 8 days e
Hearne ISD
Science
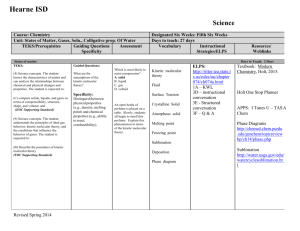
Course: General Chemistry
Units: Lab Safety, Matter & Change, Measurement & Calculations
TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions
/ Specificity
Assessment
(A) differentiate between physical and chemical changes and properties;
(EOC Readiness Standard)
(B) identify extensive and intensive properties;
(EOC Supporting Standard)
(C) compare solids, liquids, and gases in terms of compressibility, structure, shape, and volume; and
(EOC Supporting Standard)
What is a mixture?
Specificity:
Distinguish between physical properties
(e.g., density, melting point) and chemical properties (e.g., ability to react, combustibility).
(D) classify matter as pure substances or mixtures through investigation of their properties.
(EOC Readiness Standard)
Specificity:
Know that chemical changes create new substances (e.g., rusting), while physical changes do not (e.g., boiling).
College and Career Readiness
Standard
A.
Matter and Its Properties
1.
Know that physical and chemical properties can be used to describe and classify matter.
2.
Recognize and classify pure substances (elements, compounds) and mixtures. moist air.
Which of the following is an intensive physical property?
A.
color
B.
length
C.
volume
D.
mass
Which is most likely to resist compression?
A . solid
B.
liquid
C.
gas
D.
colloid
An unknown silvery powder has a constant melting point and does not chemically or physically separate into other substances. The unknown substance can be classified as a(n) .
A. element
B.
compound
C.
mixture
D.
alloy
Designated Six Weeks: First Six Weeks
Days to teach: 28 Days
Vocabulary Instructional
Strategies/ELPS
Physical Property
Chemical Property
Element
Compound
Mixture
Homogenous
Heterogeneous
Extensive property
Intensive property
Quantitative
Qualitative
Resources/
Weblinks
Classification of
Matter Lab
Chemical Changes
Lab
APPS: I Tunes U –
TASA Chem
Solids, Liquids, Gases http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gch p/liquids/character.html
Exemplar Lesson
Nuts & Bolts –
Density http://facstaff.gpc.edu/~pgore/Ph icalScience/density-demo-cans.ht
ELPS: http://ritter.tea.stat e.tx.us/rules/tac/ch apter074/ch074a.h tml
1A – KWL
3D – instructional conversation
3E - Structured conversation
3F – Q & A
Distillation Demo http://www.absorblearning.com/m dia/item.action%3bjsessionid=67
960D82BDC344300CCC856F8B
DCD1?quick=ux
Weebly Videos: http://eocvideos.weebly.co
/
Physical and Chemical
Properties http://www.educreations.com/less n/view/physical-and-chemical- properties-and- changes/4795451/?s=rUBT0D&r
=appemail
Revised Spring 2014
Hearne ISD
Science
Course: General Chemistry
Units: Lab Safety, Matter & Change, Measurement & Calculations
TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions
/ Specificity
Assessment
Designated Six Weeks: First Six Weeks
Days to teach: 28 Days
Vocabulary Instructional
Strategies/ELPS
Resources/
Weblinks
Pure Substances and
Mixtures http://www.educreations.com/les s n/view/matter/5111899/?ref=app e mail
Scientific Method, Collecting and Interpreting Data
TEKS:
2A – 2I
(2) Scientific processes. The student uses scientific methods to solve investigative questions. The student is expected to:
Guiding questions:
What is the scientific method?
How do you convert measurements into scientific notation?
(A) know the definition of science and understand that it has limitations, as specified in subsection (b)(2) of this section;
How do you convert from one unit of measurement to another?
(B) know that scientific hypotheses are tentative and testable statements that must be capable of being supported or not supported by observational evidence. Hypotheses of durable explanatory power which have been tested over a wide variety of conditions are incorporated into theories;
What are significant figures, percent error and percent yield?
Specificity:
Identify control
(C) know that scientific theories are based on natural and physical phenomena and are capable of being tested by multiple independent researchers. Unlike hypotheses, scientific theories are well-established variable, independent variable, and dependent variable
Apply the scientific method to various
Revised Spring 2014
A testable statement used for making predictions and carrying out further experiments is a
A . hypothesis.
B.
law.
C.
theory.
D.
model.
The symbols for units of length in order from smallest to largest are
A.
m, cm, mm, km.
B.
km, mm, cm, m.
C . mm, cm, m, km.
How many mm are in
3.8ft. ?
Dimensional analysis
SI Units
Significant figures
Scientific notation
Accuracy
Precision
Derived unit
Independent variable
Dependent variable
Hypothesis
Days to Teach: 15 Days
ELPS: http://ritter.tea.stat e.tx.us/rules/tac/ch apter074/ch074a.h tml
4J – prediction café
4K – writing process
5G – draw & write
Text: Modern Chemistry
Holt, 2015
Tutorial on Significant
Figures http://www.chem.sc.edu/faculty/ organ/resources/sigfigs/index.htm
Tutorial on Scientific
Notation http://www.nyu.edu/pages/mathm l/textbook/scinot.html
Hearne ISD
Science
Course: General Chemistry
Units: Lab Safety, Matter & Change, Measurement & Calculations
TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions
/ Specificity
Assessment and highly-reliable explanations, but may be subject to change as new areas of science and new technologies are developed;
(D) distinguish between scientific hypotheses and scientific theories;
(E) plan and implement investigative procedures, including asking questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting equipment and technology, including graphing calculators, computers and probes, sufficient scientific glassware such as beakers,
Erlenmeyer flasks, pipettes, graduated cylinders, volumetric flasks, safety goggles, and burettes, electronic balances, and an adequate supply of consumable chemicals;
(F) collect data and make measurements with accuracy and precision;
(G) express and manipulate chemical quantities using scientific conventions and mathematical procedures, including dimensional analysis, scientific notation, and significant figures;
(H) organize, analyze, evaluate, make inferences, and predict trends from data; and
(I) communicate valid conclusions supported by the data through methods such as lab reports, labeled drawings, graphs, journals, summaries, oral
Revised Spring 2014 hypotheses
Be able to choose the appropriate lab equipment/technology to use in their experiment
Be able to design an experiment given a problem
Guiding Questions:
How do you perform math operations involving significant figures ?
Specificity:
Use lab equipment such as graduated cylinders, burets, and balances to make measurements
Identify the precision/accuracy of different lab equipment such as beakers vs. graduated cylinders
Understand significant figures in relation to precision of a measurement
Identify the number of
Design and implement a testable hypothesis.
Designated Six Weeks: First Six Weeks
Days to teach: 28 Days
Vocabulary Instructional
Strategies/ELPS
Resources/
Weblinks
Precision vs Accuracy http://honolulu.hawaii.ed
/distance/sci122/SciLab/
5/accprec.html
Hearne ISD
Course: General Chemistry
Units: Lab Safety, Matter & Change, Measurement & Calculations
TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions
/ Specificity
Assessment reports, and technology-based reports. significant figures in a number
Describe the SI base units
Apply the rules of significant figures in calculations
Science
Designated Six Weeks: First Six Weeks
Days to teach: 28 Days
Vocabulary Instructional
Strategies/ELPS
Resources/
Weblinks
Revised Spring 2014