File
advertisement

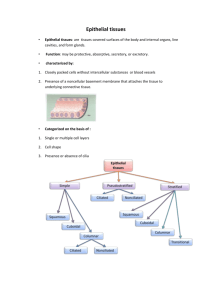
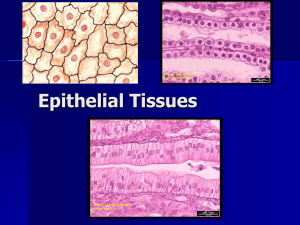
Identify the type of junction with its purpose: forms an impermeable junction; prevents molecules from passing between cells Let small molecules move directly between neighboring cells reduces tearing, twisting, stretching helps form the tight junction around apical lateral borders Location: Covers body Surfaces Lines body cavities Forms glands Functions: Secretion Selective absorption Protection Transcellular support Detection of sensation Secretion When a cell produces substances and releases those substances into the environment. Ie. Digestive tract has high secretion Selective Absorption Epithelial tissue is in direct contact with the outer environment so it selects what materials come into and out of the cell Protection Tissue in contact with the external environment has to have a protective function to protect internal tissue Ie. Skin Transcellular Transport Able to help substances travel through a certain distance Detection of Sensation Associated with nerve cells because epithelium can be found on the external part of the body; nerve cells receive stimuli Cells are usually joined by specialized cell-to-cell junctions Little or no intercellular material Don’t have a lot of extracellular material around them First the name of tissue indicates # of layers (3 types) 1. Simple – one layer of cells (extends from basement membrane to the apical surface) 2. Stratified – more than one layer of cells 3. Pseudostratified- tissue appears to be stratified, but all cells contact basement membrane so it is in fact simple Last name of tissue describes shape of cells (3 types) 1. Squamous – cells wider than tall (plate or “scale” like) 2. Cuboidal – cells are as wide as tall, as in cubes 3. Columnar – cells are taller than they are wide, like columns Naming the epithelia includes the layers (first) and the shape of the cells (second) i.e. stratified cuboidal epithelium The name may also include any accessory structures Goblet cells, cilia, keratin, etc. Special epithelial tissues (don’t follow naming convention) Psuedostratified Transitional How do you go about naming epithelial tissue? Description single layer of flat cells with disc-shaped nuclei Special types Endothelium (inner covering) slick lining of hollow organs Mesothelium (middle covering) Lines peritoneal (abdomen), pleural (lungs), and pericardial (heart) cavities Covers visceral (internal) organs of those cavities (ie. pancreas, stomach, lung, etc.) Function: Passage of materials by passive diffusion and filtration Secretes lubricating substances reducing friction from muscle in serous membranes Location: Renal corpuscles (blood filtering component in kidneys) Alveoli of lungs Lining of heart, blood and lymphatic vessels Lining of ventral body cavity Pericardium- membrane covering the heart Pleura- membrane covering the lung Peritoneum- membrane covering the abdominopelvic cavity Simple squamous lining the walls of the capillary Description single layer of cube-like cells with large, spherical central nuclei Function secretion and absorption Location kidney tubules, secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface Description single layer of column-shaped (rectangular) cells with oval nuclei Some have cilia at their apical surface May contain goblet cells (secrete mucus) Function Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances Ciliated type propels mucus or reproductive cells by ciliary action Location Non-ciliated form Lines digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts of some glands Ciliated form Lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus Identify a location where simple squamous, cuboidal or columnar tissue is found? Layers: contain two or more layers of cells Regeneration: from Basal membrane Function: protection Naming: according to the shape of cells at apical layer Description Many layers of cells – squamous in shape Deeper layers of cells appear cuboidal or columnar Thickest epithelial tissue – adapted for protection Specific types Keratinized – contain the protective protein keratin Surface cells are dead and full of keratin Non-keratinized – forms moist lining of body openings Function Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion Location Keratinized – forms epidermis Non-keratinized – forms lining of esophagus, mouth, and vagina Non-keratinized vs. Keratinized Description generally two layers of cube-shaped cells Function protection Location Forms largest ducts of sweat glands Forms ducts of mammary glands and salivary glands Description several layers; basal cells usually cuboidal; superficial cells elongated Function protection and secretion Location Rare tissue type Found in male urethra and vas deferens, largest ducts of salivary glands, nasopharynx Description All cells originate at basement membrane Only tall cells reach the apical surface May contain goblet cells and bear cilia Nuclei lie at varying heights within cells Gives false impression of stratification Function secretion of mucus; propulsion of mucus by cilia Locations Non-ciliated type Ducts of male reproductive tubes Ducts of large glands Ciliated variety Lines trachea and most of upper respiratory tract Description Basal cells usually cuboidal or columnar Superficial cells dome-shaped or squamous Function stretches and permits distension of urinary bladder Location Lines ureters, urinary bladder and part of urethra Relaxed state Stretched state Name three types of tissue, what they look at and a place where they can be found. Ducts carry products of exocrine glands to epithelial surface Include the following diverse glands Mucus-secreting glands Sweat and oil glands Salivary glands Liver and pancreas May be: unicellular or multicellular Goblet cells produce mucin Mucin + water mucus Protects and lubricates many internal body surfaces What are the two types of stratified squamous epithelial? Where can they be found? Where can simple cuboidal and stratified cuboidal be found? What is the difference in the function of each?