tissues epithelial
advertisement

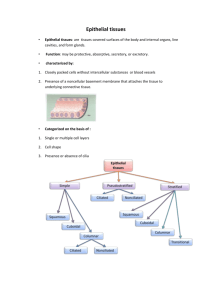
TISSUES • Tissues - cells working together to perform a common function • Histology - Study of tissues 4 BASIC TYPES • Epithelial - covers & lines surfaces, forms glands • Connective - connects tissues, provides support, stores energy reserves • Muscle - Contracts for movement, generates heat • Neural - Carries information from one part of body to another in the form of electrical impulses Epithelial Tissue - layer of cells that forms a barrier • Functions: – provides physical protection – controls permeability – provides sensations – produces secretions • Characteristics: – consists mainly of cells – consists of single layer or multiple layers – always has a free surface exposed to the environment – avascular – mitotic rate can be very high Intercellular Connections • Tight Junction - formed by fusion of cell membranes • Desmosome - thin proteoglycan layer between opposing cell membranes • Gap Junction - binding of membrane proteins CLASSIFICATION Subdivided according to shape & arrangement of cells in each type • Arrangements: • Shapes: • Squamous - flat • Cuboidal - cubed • Columnar - higher than wide • Simple - single layer of same shape • Stratified - many layers of same shape • Transitional - several layers of differing shapes http://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/media/ch20/epithelial_structure.html Bell work Questions Aug 20th 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What are the four types of tissues? Define tissue. The study of tissues is call ______________. How are Epithelial tissues named? What are the 3 basic shapes of epithelial tissues? What are the 3 basic arrangements of epithelial tissues SIMPLE SQUAMOUS (most delicate) • Locations – Alveoli in lungs – blood & lymphatic vessels • Functions – Reduce friction – Diffusion of gases – Controls permeability STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS (tough) • Locations – Surface of skin – Lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, vagina • Functions – Protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemicals SIMPLE CUBOIDAL • Locations – glands, ducts, kidney tubules, thyroid gland • Functions – protection, secretion, and/or absorption STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL (RARE) • Locations – lining of some ducts like sweat glands – Mammary glands • Functions – Protection, secretion, absorption TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM (STRETCHY) • Locations – Urinary bladder, ureters • Functions – Permits expansion & recoil after stretching SIMPLE COLUMNAR • Locations– Lining of stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes, collecting ducts of kidneys • Functions – Protection, secretion, absorption PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM • Locations - – lining of nasal cavity, bronchi, trachea • Functions – protection, secretion – Nuclei are located at varying distances from surface STRATIFIED COLUMNAR Relatively Rare • Locations – pharynx, epiglottis, anus, mammary ducts, urethra • Functions – Protection Bell work Glandular epithelium • Cells that make up glands are specialized to produce and secrete substances Types of secretions from cells • – – 1. endocrine • • Glands that secrete their products into tissues or blood Ex: Pituitary and sex glands 2. exocrine a. Merocrine: release products by exocytosis Ex: salivary glands/ pancreas b. a. Apocrine: Lose small portions of glandular bodies during secretion ex: mammary glands: fat droplets/sweat glands Holocrine: entire cell disintegrates Ex: sebaceous glands of skin (fatty mixture called sebum) Reflection • How are epithelial tissues classified? • How can you i.d. if a tissue is an epithelial?