Chapter 9 Reading Assignment
advertisement

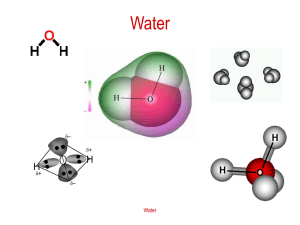
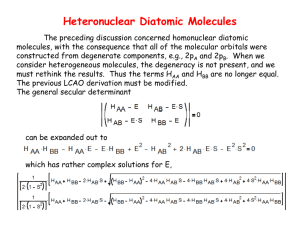
AP Chemistry Section 10.1 / Chapter 9 Reading Assignment NAME: First read section 10.1 and then chapter 9! Section 10.1 What is the difference between intramolecular bonding and intermolecular forces? Condensed states Intermolecular forces The change in states for a substance depend upon what? Dipole-dipole attraction How strong are dipole-dipole forces? Hydrogen bonding Why does hydrogen bonding have an important effect on physical properties? Explain figure 10.4. In figure 10.4 why do H2O, HF, and NH3 have unexpectedly high boiling points? If the interactions between molecules are strong what can we predict about the boiling point? Explain. London dispersion forces What happens as electrons move around the nucleus that impact intermolecular forces? Instantaneous dipole What does it mean when we say a dipole is induced? Explain table 10.2. Why do we see this trend? polarizability Chapter 9 What are two related problems with the bonding in methane, CH4? What are the two conclusions that this analysis leads to? What do we do in terms of orbitals to account for the known structure of methane? Hybridization sp3 hybridization Summarize the bonding of methane. Hybrid orbitals Explain the bonding of ethylene in terms of hybrid orbitals. sp2 Sigma bond Pi bond What does a double bond always contain? sp hybridization Explain the bonding in carbon dioxide in terms of hybrid orbitals. Skip to page 428 – Our curriculum only covers the sp3, sp2, and sp hybrid orbitals. Molecular orbital model Molecular orbitals Bonding molecular orbitals Antibonding molecular orbitals Molecular orbital theory describes covalent bonding in a manner that can capture a wider array of systems and phenomena than the Lewis or VESPR models. Molecular orbital diagrams, showing the correlation between atomic and molecular orbitals, are a useful qualitative too related to molecular orbital theory. Other aspects of molecular orbital theory are not part of the course or the AP exam. Paramagnetism Diamagnetism Heteronuclear Diatomic molecules Delocalized π bonding What is the photoelectric effect? How is PES related to the photoelectric effect? How do you calculate the energy of an electron? How does PES work? Use figure 9.50 for your explanation. What is PES useful for studying?