Unit 6 Studyguide/Review Packet: Test: B: Thursday 17 Dec 2015 A
advertisement

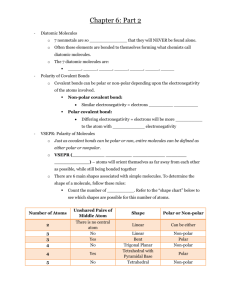
Unit 6 Studyguide/Review Packet: Test: B: Thursday 17 Dec 2015 A: Friday 18 Dec 2015 Ionic/Metallic Bonds: types of particles bonding force holding atoms together difference in electronegativity (only ionic) properties how delocalized electrons explain properties of metals Covalent Bonds: Classify bond types based on EN differences NPC: from 0 to 0.20 PC: from 0.20 to 1.67 I: greater than or equal to 1.67 What is a molecule? Determine valence electrons of atoms and molecules name/write formulas for molecules using prefixes State and Apply the octet rule Write Lewis Dot Structures Fill in the chart: see example on next page Describe the three main intermolecular forces in terms of strength and “Weird” Atoms that do not follow the octet rule: Element Symbol Number of electrons in valence: 2 hydrogen H 4 beryllium Be 6 boron B If a central atom has 5 bonded atoms it may have 10 valence eIf a central atom has 6 bonded atoms it may have 12 valence e- Write T for true and F for false. If a statement is false, replace the underlined word or phrase with one that will make the statement true, and write your correction in. True a. Dispersion forces are the only attractive forces that attract between non-polar molecules. False, can b. Molecules cannot exhibit both dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. True c. A non-polar molecule can have polar bonds. If true, then when? When the molecule is SYMMETRIC False, polar d. Water is a non-polar molecule that has polar bonds. Fill in the chart: molecular formula carbon tetrachloride CCl4 number of (total) valence e32 water H 2O 8 CHCl3 26 nitrogen tribromide NBr3 26 lewis dot structure Cl Cl - C– Cl Cl .. H-O–H .. Cl Cl - C– Cl H .. Br - N – Br Br number of bonded atoms (B) number of lone pair (E) type of molecule (A B E) molecular shape polarity of molecule (P or NP) 4 0 AB4 tetrahedral NP 2 2 AB2E2 bent P 4 0 AB4 tetrahedral P 3 1 AB3E trigonal pyramid P Practice: 1. Pairs of electrons that bond two atoms in a molecule are called ___shared pairs_____. 2. Pair of electrons that are unshared are called lone pair. 3. Because each of the bond angles of methane equals 109.5⁰, its molecular shape is a perfect tetrahedron. 4. Define “dipole” in your own words! DO NOT use the same definition from your notes, paraphrase and simplify! polar molecule 5. Are the bonds in a polar molecule arranged symmetrically or asymmetrically? 6. Matching (write the roman numeral beside the letter it matches) iii a. a non-polar molecule in which the charge i. dispersion forces distribution is very briefly asymmetrical i b. forces generated by instantaneous dipoles ii. dipole-dipole forces v c. forces between molecules iii. instantaneous dipole iv d. forces within a molecule iv. intramolecular forces ii e. attractive forces between two molecules v. intermolecular forces of the same or different substance that are both “permanent” dipoles