DW 14-4
advertisement

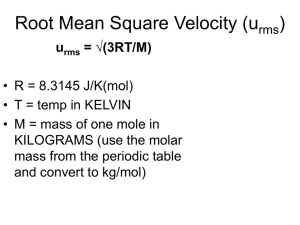
Name ___________________________________ Date ______________________ Class ______________________ Directions: Work the following problems based on Chapter 14 Section 4. Title: Daily Work 14-4 Match each description in column B to the correct term in column A. Column A Column B _____ 1. Partial pressure a. The pressure exerted by each gas in a gaseous mixture. _____ 2. Effusion b. The escape of a gas through a tiny hole in its container. _____ 3. Graham’s law of effusion c. The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its formula masses. 4. In a mixture of gases, how is the total pressure determined? 5. What is the effect of molar mass on rates of diffusion and effusion? 6. How is the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture calculated? 7. What distinguishes effusion from diffusion? How are these processes similar? 8. How can you compare the rates of effusion of two gases in a mixture? 9. Explain why the rates of diffusion of nitrogen gas and carbon monoxide are almost identical at the same temperature? 10. A gas mixture containing oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide has a total pressure of 32.9kPa. If PO2=6.6kPa and PN2=23.0kPa, what is PCO2? 11. Which gas effuses faster at the same temperature: molecular oxygen or atomic argon? 12. Calculate the ratio of the velocity of helium atoms to the velocity of neon atoms at the same temperature. 13. Calculate the ratio of the velocity of helium atoms to the velocity of fluorine molecules at the same temperature. 14. Explain, using kinetic theory, why molecules of low molar mass diffuse more rapidly than molecules with a higher molar mass.