Molecular Compostion of Gases
advertisement

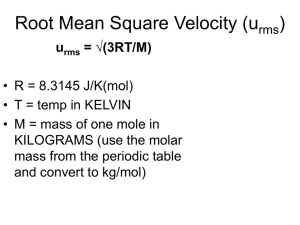
Molecular Compostion of Gases Effusion and Diffusion Objectives 1. State graham’s law of effusion 2. Determine the relative rate of effusion of two gases of known molar masses. Effusion and Diffusion Diffusion – mixing of particles as a result of random motion. Effusion – process by which gas particles pass through a tiny opening. Graham’s Law of Effusion • The rates of diffusion and effusion depend on the velocity of gas particles. • Velocity of gas particles varies inversely with mass For two different gas samples at the same temperature, particles of each gas have the same average kinetic energy. Therefore: 1 2 m Av 2 A 1 2 2 mBvB Graham’s Law of Effusion Multiplying both sides by two and considering that mass is proportional to Molar mass…. M Av or… M Bv 2 A 2 vA 2 vB vA vB M B M A M B M A 2 B Graham’s Law of Effusion • The rates of effusion of gases at the same temperature and pressure are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molar masses. Graham's Law Demonstration - Animated - YouTube Because the rate of effusion is directly proportional to molecular velocities: rate of effusion of A rate of effusion of B Also: rate of effusion of A rate of effusion of B M B M A M B M A density B density A Sample Problems 1. At 25oC, the average velocity of oxygen molecules is 420 m/s. What is the average velocity of helium atoms at the same temperature? 2. At a certain temperature, hydrogen molecules move at an average velocity of 1.84 x 103 m/s. Estimate the molar mass of a gas whose molecules have an average velocity of 312 m/s. Sample Problems 3. Nitrogen effuses through a pinhole 1.7 times as fast as another gaseous element at the same conditions. Estimate the other element’s molar mass, and determine its probable identity. 4. Determine the molecular mass ratio of two gases whose rates of diffusion have a ratio of 16:1. Review Questions 1. When a cylinder of oxygen is left standing in the sun, the temperature of the gas reaches 42oC. The cylinder has a volume of 10.0 L and contains 128 g of oxygen. What is the pressure in atmospheres inside the cylinder? 10.3 atm 2. Sulfur dioxide has a density of 2.927 g/L at STP. What is its density at a pressure of 108 kPa and 50.0oC? 2.65 g/L 3. What would be the density of 1.0 L of hydrogen at STP? What would be the density of 1.0 L of oxygen at STP? 0.089 g/L and 1.4 g/L 4. An unknown gas effuses at 0.850 times the effusion rate of nitrogen dioxide. Estimate the molar mass of the unknown gas. 64 g/mol Review Questions 5. A gas sample that has a mass of 0.993 g occupies 0.570 L. Given that the temperature is 281 K and the pressure is 1.44 atm, what is the molar mass of the gas? 27.9 g/mol 6. The density of a gas is 3.07 g/L at STP. Calculate the gas’s molar mass. 68.8 g/mol 7. Compare the rates of diffusion of carbon monoxide and sulfur trioxide. CO is 1.7 times faster than SO3