Introduction to Cells
advertisement
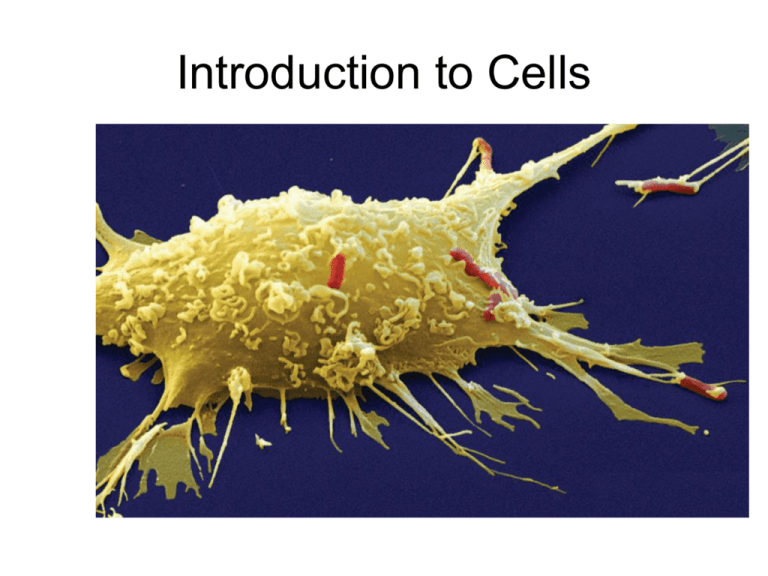
Introduction to Cells Why does this cell look like a fried egg? • Cells vary greatly in their size and shape. • A cell’s shape reflects its function. • Cells can be branched, flat, round, or rectangular. – The Cell theory has three principles. • All organisms are made of cells. • All living cells are produced by other living cells. • The cell is the most basic unit of life. – All cells share certain characteristics. • All cells are enclosed by a membrane. • All cells are filled with cytoplasm. • All cells have DNA. • All cells have ribosomes. cell membrane cytoplasm Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) • There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. – Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. nucleus – Eukaryotic cells have membranebound organelles. organelles cell membrane – Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. – Prokaryotic cells do not have membranebound organelles. nucleus organelles cell membrane cytoplasm Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Cytoskeleton •The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its shape, and organize its parts. Click to animate the image. A B C D • Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins. – The nucleus stores genetic information. The Nucleus B C D A The nucleolus is a structure within the nucleus where ribosomes are made. – Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum • rough endoplasmic reticulum • smooth endoplasmic reticulum • Rough ER has ribosomes and takes part in the production of protein • Smooth ER lacks ribosomes. Smooth ER makes lipids and breaks down drugs and alcohol. – Ribosomes link amino acids to form proteins. – Ribosomes link amino acids to form proteins. – Vesicles are membrane-bound sacs that hold materials. – Vesicles help maintain homeostasis by storing and releasing a variety of substances as the cell needs them. Golgi apparatus Protein Processing Making and Exporting Proteins • The ribosomes located on the rough ER make proteins which then cross into the membranes of the ER. The ER membrane then pinches off and forms a vesicle around the proteins. • Vesicles transport the proteins from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus, where they are modified by enzymes and repackaged in new vesicles. • These new vesicles transport the modified proteins to the cell membrane to be released outside the cell. Lysosomes • A lysosome is a vesicle produced by the Golgi apparatus that contains enzymes that break down large molecules. • Lysosomes recycle old or damaged organelles and digest food particles to provide nutrients for the cell. Mitochondrion • Mitochondria supply energy to the cell. • Mitochondria use energy from organic compounds to make ATP. • Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials. Centrioles are tubes found in the centrosomes. • Centrioles help divide DNA. • Centrioles form cilia and flagella. • Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts. – A cell wall provides rigid support. – Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy.