Biology I Core 40 Test Review: Cellular Structure
advertisement
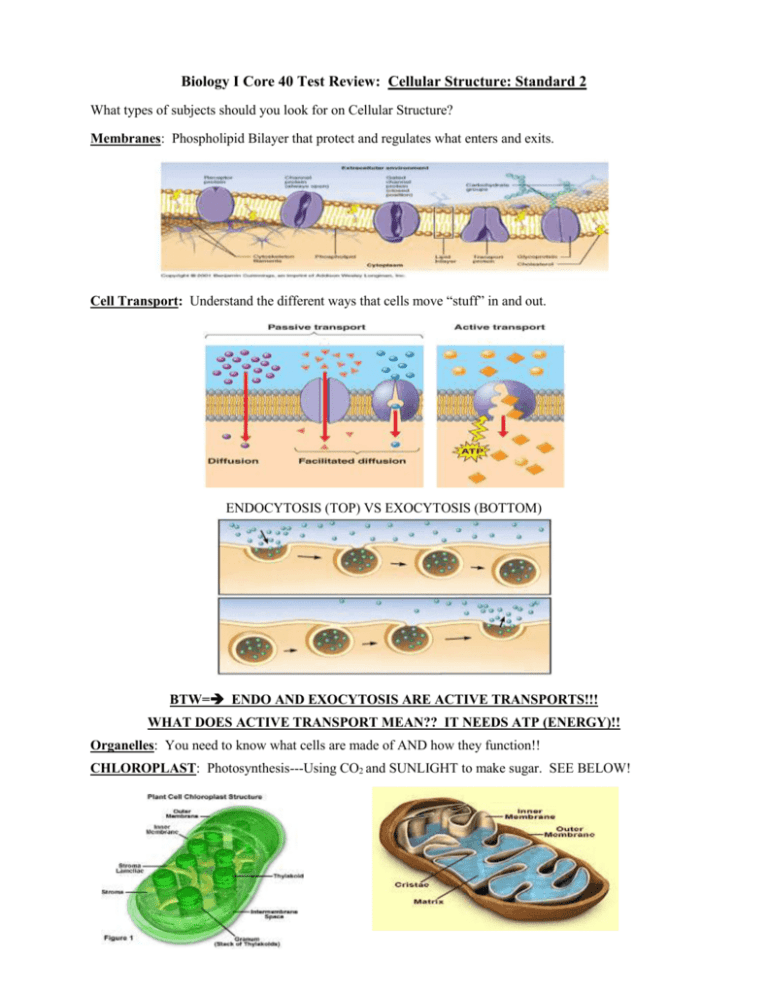
Biology I Core 40 Test Review: Cellular Structure: Standard 2 What types of subjects should you look for on Cellular Structure? Membranes: Phospholipid Bilayer that protect and regulates what enters and exits. Cell Transport: Understand the different ways that cells move “stuff” in and out. ENDOCYTOSIS (TOP) VS EXOCYTOSIS (BOTTOM) BTW= ENDO AND EXOCYTOSIS ARE ACTIVE TRANSPORTS!!! WHAT DOES ACTIVE TRANSPORT MEAN?? IT NEEDS ATP (ENERGY)!! Organelles: You need to know what cells are made of AND how they function!! CHLOROPLAST: Photosynthesis---Using CO2 and SUNLIGHT to make sugar. SEE BELOW! MITOCHONDRIA: Cell Respiration----Making ATP by breaking down sugar. Notice how the chloroplast has stacks of sacks called thylakoids. Now you can fit more!!! STRUCTURE always relates to FUNCTION: Cells and organelles are arranged a certain way because they have evolved to be efficient. It makes sense to fold the ER up in order to fit more in the cell. It makes since to fold the mitochondrial membrane up to fit more inside. These both work to increase the SURFACE AREA of the working parts. CO2 + H2O + Sunlight ======== Glucose (Sugar) + H20 This equation is the key to energy for living organisms Ribosomes: The “machines” that translate mRNA into a protein (Protein Synthesis). Protein, Protein, Protein: Everything that does work (building, digesting, moving, etc) is made of protein. IT RULES!! Enzymes, flagella, cilia, receptors cytoskeleton---EVERYTHING THAT IS MECHANICAL. *****BTW=> Who makes proteins? Based on what code/recipe/directions? Diversity of Cells: For example---You are made of 35 trillion cells. Do you think they are all the same? There are different types of cells because they have different types of functions. Below are types of cells in your body. They all have different types of organelles and functions. For example, muscle and nerve cells are LOADED with mitochondria……..WHY? Multiple Choice 1. Muscle cells use a lot of energy so which of the organelles below would you find a large quantity of inside these specialized cells? a. Lysosomes c. Ribosomes b. Gogi Bodies d. Mitochondria 2. Which of the following organelles is responsible for protein synthesis? a. Lysosomes c. Ribsomes b. Mitochondria d. Vacuoles 3. Severely dehydrated person is often given intravenous saline injections. Saline (0.9% NaCl) has the same electrolyte concentration as human cells. What would happen if pure water was introduced into the body instead of saline a. The cells would gain water and swell b. The cells would lose water and shrivel c. The cells would become impermeable to sodium (Na+) ions d. The cells would become impermeable to chlorine (Cl-) 4. What two organelles are responsible for transport and packaging of proteins in the cell? a. Lysosome and chloroplast b. Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi c. Chloroplast and Ribosome d. Chromosomes and Nuclear Pores 5. Water moves across a permeable membrane due to: a. Moving from a high concentration to a lower concentration b. Moving from a lower concentration to a higher concentration c. Being transported by a protein d. Moving through protein channels 6. Animal cells have all the following cell parts except: a. Mitochondria c. Cell Wall b. Chloroplast d. B and C are correct 7. When a cell moves molecules across the membrane through a channel protein and uses ATP for the movement it is called: a. Diffusion c. Facilitated Diffusion b. Osmosis d. Active Transport 8. Which of the following is not a form of active transport? a. Osmosis c. Exocytosis b. Endocytosis d. Phagocytosis 9. When molecules are engulfed by the cell membrane and brought into the cell it is called: a. Osmosis c. Exocytosis b. Endocytosis d. Diffusion 10. The plasma membrane is made mostly of ________________ a. Proteins c. DNA b. Phospolipids d. Carbohydrates Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Some are flat, some are square, and some have all sorts of shapes 11. What is the main reason for the diversity of cells a. Different genes of DNA control different cells b. Cells vary greatly based on structure and function c. Cells carry out a divers range of tasks d. All of the above are correct Open Response 1. List and explain 3 ways that cells transport materials in and out a. b. c. 2. Give the name and function of two of the structures above: a. b. 3. Describe (4) differences between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: a. b. c. d. 4. Describe 2 reasons why a nerve cell is different from a skin cell (hint): Function & Genetics. a. b.