File
advertisement

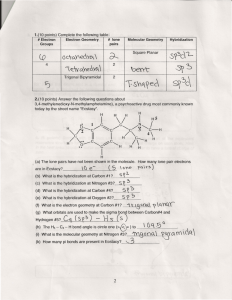
Name: __________________________________________ Molecular Geometry VSEPR Lab Purpose: To determine the geometry, bond angles, and hybridization of various compounds. Pre-Lab: 1. Define VSEPR. 2. Identify by name and sketch the ten VSEPR shapes. 3. Explain the difference between bonded and nonbonded electron pairs. 4. Justify how to determine molecular polarity. Procedure: Draw the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Count the number of bonded and non-bonded pairs around the central atom. Determine the piece needed to create your molecule (linear, planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, or octahedral). Then create your molecule and decide its overall geometry, bond angles, and hybridization. An example is given. Molecule H2O CO2 SO2 CH4 NH3 OF2 HF PCl5 SF4 ClF3 XeF2 Lewis Structure Pairs on the Central Atom Symmetrical Piece Needed Geometry 2 single bonds 2 lone pairs Tetrahedral Bent Bond Hybridization Angle 109.5 Molecule Lewis Structure Pairs on the Central Atom Symmetrical Piece Needed Geometry Bond Hybridization Angle SF6 BrF5 XeF4 Questions: 1. For the following compounds draw the Lewis structure and give the geometry. What do they all have in common? N2 Br3CO2 2. For the following compounds with 4 elements, draw the Lewis structure, give the geometry, and state what property made them all different shapes: BF3 NH3 ClF3 3. For the following compounds with 5 elements, draw the Lewis structure, give the geometry, and state what property made them all different shapes: SiH4 SeI4 XeI4 4. For the following compounds with 6 elements, draw the Lewis structure, give the geometry, and state what property made them all different shapes: AsF5 IF5 5. For the following compounds, draw the Lewis structure, give the geometry, and show any dipole moment with an arrow: PCl6- PCl4+ IF3 TeI4 BrCl5 TeF4