Study Guide Environments and Habitats in the Regions of Georgia
advertisement

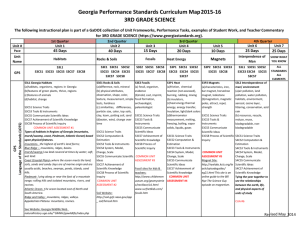
Study Guide Environments and Habitats in the Regions of Georgia Standard: S3L1: Students will investigate the habitats of different organisms and the dependence of the organisms on their habitat. By the end of this study you should be able to: Differentiate between the habitats of Georgia Identify features of green plants that allow them to live in each region of Georgia Identify feature of animals that allow them to live in each region of Georgia Describe what will happen to an organism if the habitat is changed. Vocabulary: environment –Everything that is around a living thing. ecosystem – All the living and nonliving things that interact in a place. habitat – The place where a plant or animal lives. organism – Any living thing. drought – a long period of time with very little rain. balance – not too many and not too few of a kind of living thing. Environments A variety of environments and ecosystems can be found in the state of Georgia. An environment is everything that surrounds a living thing. Plants and animals use what is found in their environment to meet their needs (food, water, oxygen, shelter). Living things interact with none living things within these environments to create ecosystems. Within each ecosystem each living thing has its own habitat. An example of this would be a fresh water environment such as a pond ecosystem. Many animals live in and around the pond, for example water lilies growing in the water, reeds and grasses growing along the edge, fish living under the water, frogs and turtles living in and out of the water, with wild geese or ducks living in nests built in grassy areas nearby. The chart below describes the landscape, soil, vegetation and animal habitats of each region. Region Mountains Landscape/Climate Animals Plants/Soil There are mountains, valleys and ravines along with many waterfalls. The elevation is higher than the rest of Georgia which causes changes in the plants. Spring and summer bring warm days and cool nights. Winters can be cold with some snowfall. Deer, black bears, wild turkeys, raccoons, bats, and foxes roam the mountains. Trout can be found in mountain streams while bass and bluegill fish live in the lakes. Piedmont This is an area of rolling hills. Piedmont means “foot of the mountain.” The piedmont has forests, lakes and rivers. The climate of this area is slightly milder than that of the mountain region. Squirrels, chipmunks, rabbits, coyote, cardinals, blue-jays and owls are often found in the forested land of this region. Mountain laurel and wild azaleas along grow abundantly on the sides of mountains. Hard-wood trees such as maple, beech and dogwoods give way to smaller deciduous fir trees in the higher elevations. The soil here is rocky but can be rich in nutrients. Apples are a common crop for this area. A thick layer of red clay soil covers much of the piedmont region. The forests contain a mixture of hardwoods and pines such as maples, elms and birches. Coastal Plains This is a low flat region going from well-drained gently rolling hills to poorly drained flatland. The climate in this region can get quite hot during the spring and summer months. During the winter this region can dip to the freezing mark and experience frost, but snowfall is rare. The wetlands consist of marshes and swaps covered in still or slow-moving water. The climate of this region is hot and humid, with temperatures raring dipping to freezing mark. This is the coastline area of Georgia that meets the Atlantic ocean. This is area is naturally sandy with a climate that can be hot and humid, with ocean breezes and winds. Armadillo, deer, wild hogs, and rattlesnakes are common in the pine forests located in this region. Tall pine trees are common in this area. Their shallow root system is well suited for the sandy soil. Farming is popular due to the flat landscape. Peanuts, pecans and cotton are a few of the most common crops. Alligators, marsh rabbits, otters, snakes, frogs, black bears, wild hogs can be found in the wetland areas. Insects such as dragonflies, mosquitoes and deer flies are also common. Shrimp, crab, redfish, flounder, and sea trout can be found in the waters off shore. Sea turtles also make their home along the Georgia coast. Plants must be able to grow in waterlogged areas. Plants with long stems such as water lilies, and marsh grasses are common. Cypress trees grow well because they have roots that stick out of the water to take in air. Seaweed and algae grow in Georgia’s ocean waters, and sea grasses such as sea oats are common on Georgia beaches. Live oak trees with Spanish moss, and palmetto plants are found slightly inland. Wetlands Ocean Suggested Websites: http://www.teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?video_id=152755 http://museum.nhm.uga.edu/index.php?page=content/education/habitats/habitats




![HabitatsOrganismsnewsletter[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007214856_1-1740411bb520253279cc4e06031ca006-300x300.png)