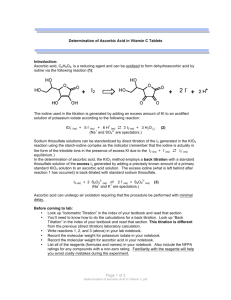
Experiment 5: Iodimetric Titration of Vitamin C
advertisement
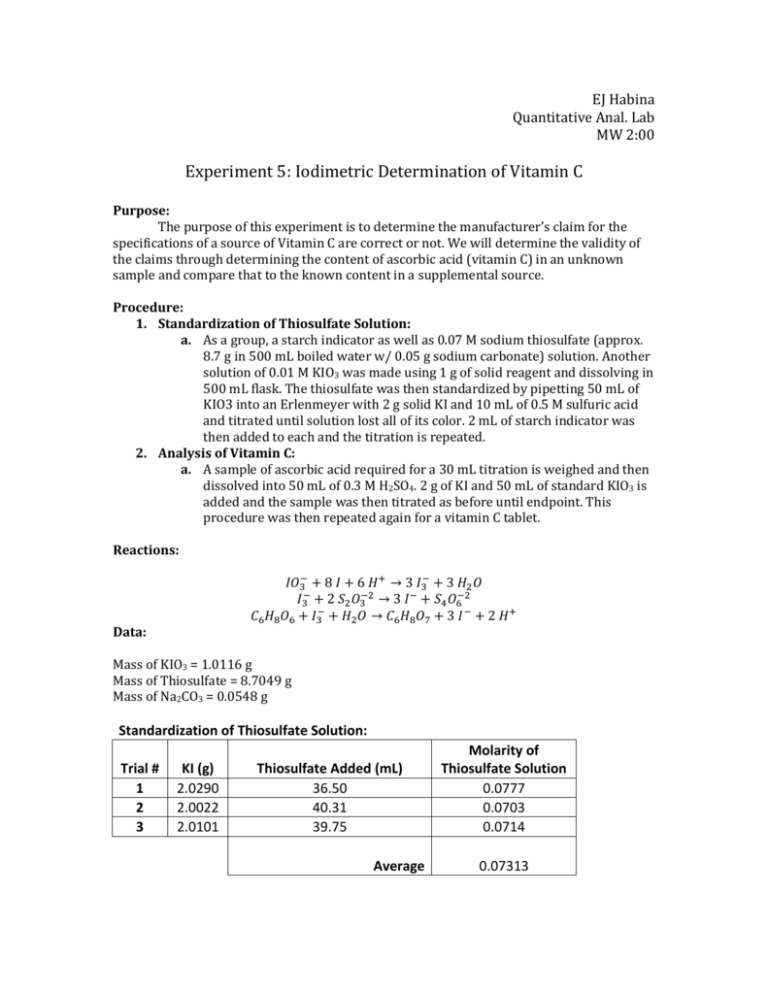
EJ Habina Quantitative Anal. Lab MW 2:00 Experiment 5: Iodimetric Determination of Vitamin C Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to determine the manufacturer’s claim for the specifications of a source of Vitamin C are correct or not. We will determine the validity of the claims through determining the content of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in an unknown sample and compare that to the known content in a supplemental source. Procedure: 1. Standardization of Thiosulfate Solution: a. As a group, a starch indicator as well as 0.07 M sodium thiosulfate (approx. 8.7 g in 500 mL boiled water w/ 0.05 g sodium carbonate) solution. Another solution of 0.01 M KIO3 was made using 1 g of solid reagent and dissolving in 500 mL flask. The thiosulfate was then standardized by pipetting 50 mL of KIO3 into an Erlenmeyer with 2 g solid KI and 10 mL of 0.5 M sulfuric acid and titrated until solution lost all of its color. 2 mL of starch indicator was then added to each and the titration is repeated. 2. Analysis of Vitamin C: a. A sample of ascorbic acid required for a 30 mL titration is weighed and then dissolved into 50 mL of 0.3 M H2SO4. 2 g of KI and 50 mL of standard KIO3 is added and the sample was then titrated as before until endpoint. This procedure was then repeated again for a vitamin C tablet. Reactions: 𝐼𝑂3− + 8 𝐼 + 6 𝐻 + → 3 𝐼3− + 3 𝐻2 𝑂 𝐼3− + 2 𝑆2 𝑂3−2 → 3 𝐼 − + 𝑆4 𝑂6−2 𝐶6 𝐻8 𝑂6 + 𝐼3− + 𝐻2 𝑂 → 𝐶6 𝐻8 𝑂7 + 3 𝐼 − + 2 𝐻 + Data: Mass of KIO3 = 1.0116 g Mass of Thiosulfate = 8.7049 g Mass of Na2CO3 = 0.0548 g Standardization of Thiosulfate Solution: Trial # 1 2 3 KI (g) 2.0290 2.0022 2.0101 Thiosulfate Added (mL) 36.50 40.31 39.75 Average Molarity of Thiosulfate Solution 0.0777 0.0703 0.0714 0.07313 Analysis of Vitamin C: Ascorbic Acid w/ Sulf. Acid Trial # Ascorbic Acid (g) 1 KI (g) 0.1871 Thiosulfate Added (mL) Wt. % of Ascorbic Acid 2.0052 12.40 90.85% KI (g) 2.0900 2.0220 2.0042 Thiosulfate Added (mL) 14.8 14.8 14.9 Wt. % of Vitamin C 82.32% 82.32% 82.32% KIO3 & KI w/ Thiosulfate Trial # 1 2 3 Vitamin C (g) 0.1878 0.1875 0.1874 Calculations: Molarity of KIO3: 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 × Ex: 1.0116 𝑔 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 1 × = 𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 214.00 𝑔 0.05 𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 1 × = 0.009454 𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 214.00 𝑔 0.05 𝐿 Molarity of Sodium Thiosulfate: 𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 × 0.05 𝐿 × Ex: 0.009454 𝑀 × 0.05 𝐿 × 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1𝑔 × × = 𝑀 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜𝑠𝑢𝑙𝑓𝑎𝑡𝑒 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼𝑂3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 𝐴𝑑𝑑𝑒𝑑 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1𝑔 × × = 0.0777 𝑀 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜𝑠𝑢𝑙𝑓𝑎𝑡𝑒 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼𝑂3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 0.0365 𝐿 Amount of Ascorbic Acid Required: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 176.12592 𝑔 𝑀 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜𝑠𝑢𝑙𝑓𝑎𝑡𝑒 × 0.03 𝐿 × × × − 2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 = 𝑔 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 Ex: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 176.12592 𝑔 × × − 2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 = 0.18757 𝑔 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 0.07313 𝑀 × 0.03 𝐿 × Weight % of Ascorbic Acid (also for Vitamin C): 𝐿 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 𝐴𝑑𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑀 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 × × × = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 1 1 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 × 0.05 𝐿 × 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 = 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐼3 − 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 176.1256 𝑔 × = 𝑔 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 𝑔 𝑜𝑓 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 × 100 = 𝑊𝑡. % 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 Ex (using Trial 1 data): 0.0124 𝐿 0.07313 𝑀 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 × × × = 0.000453 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 1 1 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑜. 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 0.009454 𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 × 0.05 𝐿 × 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 = 0.001418 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 0.001418 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐼3 − 0.000453 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 = 0.000965 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3 𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 176.1256 𝑔 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 = 0.16997 𝑔 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 0.000965 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 × 0.16997 𝑔 𝑜𝑓 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 × 100 = 90.85 % 0.1871 𝑔 Claimed Manufacturer Wt. %: 0.25 𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 × 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 × 0.25 𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 × 0.52 𝑔 × 1 × 100 = 𝑊𝑡. % 0.303 𝑔 1 × 100 = 42.9 % 0.303 𝑔 Conclusion: The purpose for this experimental procedure was to determine the content of both commercial Vitamin C tablet as well as reagent grade ascorbic acid. After completing the procedure, the results for the amount of reagent grade ascorbic acid was calculated to be 90.85 %, which is a desired value due to the assumed purity of a reagent grade chemical. As for the accuracy of the commercial vitamin C tablet results, the value of 82.3 % from the data in this procedure was much higher than the calculate manufacturer claimed weight percent of 42.9 %. As for the particles that did not dissolve, they are what are known as fillers. These act as a supplemental substance in tablets so that the tablet can reach a desired size, weight, etc.