維他命C含量測定
advertisement

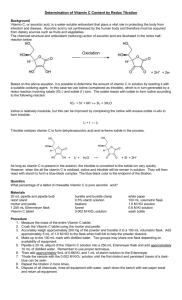
Determination of Vitamin C 維他命C含量之測定 • Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a water soluble antioxidant, and plays a vital role in protecting the body. • It can be obtained from citrus fruits, tomatoes, potatoes, and fresh vegetables, particularly from red and green peppers. • The minimum daily requirement is 30 mg, the recommended daily allowance is 60-70 mg. • The formula for ascorbic acid is C6H8O6 and the structures for the reduced form and for the oxidized form (dehydroascorbic acid) are • The amount of ascorbic acid can be determined by a redox titration with a standardized solution of iodine. The iodine is reduced by the ascorbic acid to form iodide. 1 IO3- + 5 I - + 6 H+ 3 I2 + 3 H2O C6H8O6 + I2 C6H6O6 + 2 I- + 2 H+ • The titration end point is reached when a slight excess of iodine is added to the ascorbic acid solution. • The reaction with potassium iodate titration utilizes starch as the indicator. • When all of the ascorbic acid has reacted with the KIO3, the excess KIO3 oxidizes the KI produced in the reaction (which is colorless) to I2 which forms a deep blue color with the starch indicating that the reaction is complete. Procedure Part 1: Preparation of iodine solution : 0.1g of potassium iodate and 2g of potassium iodide were weighted accurately by an electric balance. Then was dissolved in 50 mL distilled water and 1 mL conc. HCl. It was then dissolved in a volumetric flask to make up to 250 mL iodine solution. Part 2: Preparation of vitamin C Accurately weigh out a sample of ascorbic acid (about 0.3 g) . The sample was dissolved in distilled water. It was made up to 100 mL by a volumetric flask. Part 3:Titration of iodine solution against vitamin C. • The burette was filled up with the standard iodine solution. • 25 mL of the vitamin C solution, were pipetted out and added into a conical flask. Starch was added as an indicator in this moment. • Titrate with the standard iodine solution until the first appearance of a blue endpoint. • Do a total of three accurate titrations with one standard solution. Determine the average molarity of your sample. Determine the standard deviation of that average. 試題規範 • 操作時間:三小時三十分 • 操作說明:碘酸根離子和過量之碘離子 於酸性下反應,可生成碘,利用其與維 他命C之氧化還原反應,可用以定量維他 命C。 操作步驟 1. 碘溶液之配製: (1) 精秤約0.1 g乾燥之KIO3,放入150 mL燒杯 中,並加入約2 g KI。 (2) 以50 mL去離子水及1 mL濃鹽酸將其完全溶 解,並定量至250 mL。 2. 維他命C之定量: (1) 精秤維他命C約0.3 g,以去離子水溶解,並 定量至100 mL。 (2) 取上述溶液25 mL,加入1 mL 3%偏磷酸溶 液,再加入1mL 0.5%澱粉溶液。 (3) 用碘溶液滴定至終點,再重覆滴定二次,求 維他命C之平均值。 分析原理 • 碘酸鉀中之碘酸根離子(IO3-)與碘化鉀之碘 離子(I-,過量)在酸性(濃鹽酸)下反應可 生成碘分子(I2)(如此配製而成之溶液稱為碘 溶液)。 • 而碘分子則會與維他命C反應後還原為碘離子, 因此可以用碘溶液當做標定液,並用澱粉當做 指示劑來測定維他命C的含量。 • 當碘溶液剛開始滴入到維他命C溶液中時,因為 維他命C將碘溶液中的碘分子還原為碘離子,所 以溶液雖會有藍色出現但很快會消失 • 而直到滴定終點,當維他命C已耗盡,則碘分子 與澱粉液產生藍色且維持30秒不褪色。 • 由此滴定結果可進一步計算求出溶液中 維他命C的含量。其反應方程式如下: IO3- + 5 I- + 6H+ → 3 I2 + 3 H2O C6H8O6 + I2 → C6H6O6 + 2 I- + 2H+ (維他命C) (去氫維他命C) 計算 • 由以上反應方程式知一莫耳碘酸鉀反應之後可 產生三莫耳的碘分子,而一莫耳碘分子則恰可 與一莫耳之維他命C反應。其計量方程式如下: 操作指引 : (一)碘溶液之配製 精秤約0.1 g乾燥之KIO3 放入150 mL燒杯內 再加入約2 g KI 加50 mL去離子水及1mL濃鹽酸, 並攪拌將之溶解 將溶解之溶液倒入250 mL量瓶中 用水潤洗燒杯數次,並將洗液併入量 瓶中(注意水勿過量) 將量瓶加水稀釋至刻度線,並倒置震盪均勻 操作指引 : (二)維他命C之定量 精秤約0.3g 之維他命C 放入150 mL燒杯內,加水並攪拌將之溶解 將溶解之溶液倒入100 mL量瓶中 用水潤洗燒杯數次,並將洗液併入量瓶中 (注意水勿過量) 將量瓶加水稀釋至刻度線,並倒置震盪均勻 以 球型 吸量管吸取25 mL試樣 溶液於250 mL錐形瓶中 加入1 mL 3%偏磷酸溶液,再加入 1 mL 0.5%澱粉溶液 用碘溶液滴定至終點,再重覆滴定兩 次(至產生藍色維持30秒不褪色,即 達滴定終點) 記錄碘溶液用量 結果報告 相對標準偏差(standard deviation) Σ X i X n 1 2 SD= X :數據平均值 A.碘溶液之配製 HCl (1)精秤約0.1g乾燥之 KIO3放入150mL燒杯中 並加入2g的KI。 (2)以約50mL純水將其 完全溶解後再加入 1mL濃鹽酸。再以定 量瓶稀釋至250mL。 B.維他命C之定量 (3)精秤維他命C 約0.3g以純水溶 解之並以量瓶定 量稀釋至100mL。 (4)以移液管精取上述溶液 25mL,再以吸量管加入 1mL3%偏磷酸溶液,再加 入1mL0.5%澱粉溶液。 (5)用碘溶液滴定至 終點,再重複滴定 二次,求維他命C 之平均值。