Experiment 5: Iodimetric Titration of Vitamin C
advertisement

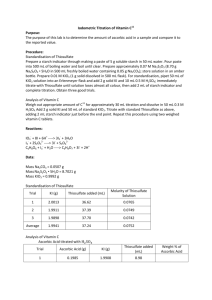
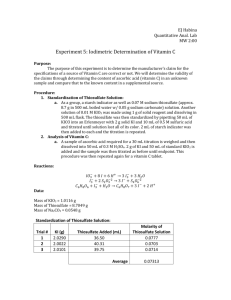
Experiment 5: Iodimetric Titration of Vitamin C Objective: The purpose of this lab is to determine amounts of Vitamin C in a product compared to their nutritional claims. Procedure: Standardization of Thiosulfate Prepare Starch Indicator using 5g soluble starch in 50mL water Add to 500mL boiling water and boil until clear Dissolve 8.70g Na2S2O3 5H2O in 500mL boiled water with 0.05g Na2CO3 Prepare 0.01M KIO3 by dissolving 1g solid reagent in a 500mL volumetric flask Standardize Thiosulfate by adding 50mL of KIO3 into an Erlenmeyer Flask with 2g KI and 5mL of 6.0M H2SO4 Titrate to a pale yellow color with thiosulfate Add 5mL of Starch indicator and complete titration Analysis of Vitamin C Weigh approximate amount of ascorbic acid needed for 30mL titration and dissolve it in 50mL of 0.3M H2SO4 Add 2g KI and 50mL of standardized KIO3 Titrate with standardized thiosulfate adding 5mL of starch indicator before completion Repeat procedure for 2 weighed vitamin C tablets Equations: 6H+ + IO3- + 8I- → 3I- + 3H2O I3- + 2S2O32- → 3I- + S4O62C6H8O6 + I3- + H2O →C6H8O7 + 3I- + 2H+ Data: Standardization of the Thiosulfate Mass of Soluble Starch (g) Mass of Na2S2O35H2O (g) Mass of Na2CO3 (g) Mass of Solid Reagent (g) 5.0151 8.7012 0.0514 1.0030 Trial Mass of KI (g) 1 2 3 2.0010 2.0053 2.0117 Average Volume Thiosulfate Used (mL) 7.7 7.2 7.6 M Thiosulfate 0.065 0.069 0.066 0.067 Vitamin C Data Trial Mass (g) Mass of KI (g) Ascorbic Acid CVS Tablet Nature’s Bounty Tablet 0.1383 0.1948 0.1993 2.0057 2.0081 2.0034 Thiofulfate Volume (mL) 16.8 12.7 10.6 Vitamin C in Sample (g) 0.1649 0.1892 0.2015 % Vitamin C in Sample 119.2 97.13 101.1 Calculations: Title M Na2S2O3 Formula Calculation 𝑀 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 3𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 2𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 1 = 𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 (𝐿 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 ) ( )( ) − )( 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 𝐿 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 Moles of I3- Excess moles of I3- Reacted moles of I3Mass of Vitamin C % Vitamin C in Sample 3𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐼3− 𝑀𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3− = 𝑀𝐾𝐼𝑂3 (𝐿 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 ) ( ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 𝐸𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝐼3− 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂32− 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− = 𝑀 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 (𝐿 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 ) ( )( ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 2𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂32− 𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 − 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑉𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝐶 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑉𝑖𝑡𝐶 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐴𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑏𝑖𝑐 𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑑 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐼3− ( )( ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝐴 % 𝑉𝑖𝑡 𝐶 = ( 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑣𝑖𝑡 𝐶 ) ∗ 100 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑆𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 𝑀 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 = 0.01 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 (0.050𝐿 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 ) 3𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 2𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 1 ( )( ) − )( 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 0.0077𝐿 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 =0.065M 3𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐼3− 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐼3− = 0.01𝑀 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 (0.050𝐿 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 ) ( ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 − = 0.0015𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 𝐸𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝐼3− = 0.067𝑀 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 (0.0168𝐿 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂32− 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− ( )( ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 2𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂32− = 0.0005628𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− = 0.0015𝑚𝑜𝑙 − 0.0005628𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 0.0009372𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑉𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝐶 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑉𝑖𝑡𝐶 176.0𝑔 𝐴𝐴 = 0.0009372𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− ( )( ) 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝐴 = 0.1649𝑔 0.1649𝑔 𝑣𝑖𝑡 𝐶 % 𝑉𝑖𝑡 𝐶 = ( ) ∗ 100 = 119.2% 0.1383𝑔 𝑆𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 Conclusion: The percent vitamin C obtained is way too high meaning there is great error. For the CVS tablet there was 97.13% and Nature’s Bounty had 101.1%. Both of these values are much higher than the claims on the nutritional label. The main problem with this lab occurred before the actual experiment started. The lab preps are incompetent and did not know how to create the correct molarity solutions to be used. The actual value had to be estimated because the value was unknown and off from its claimed molarity. This caused problems in the calculations with the rest of the moles used because the values are based off the molarity of this original solution. Also in the procedure half of a tablet was used and this may not have been perfectly half of the tablet. Finally, in titrating the sample the tablet had to be dissolved first. If it was not fully dissolved the equivalence point may have shown up earlier than expected.