Experiment Five - Iodimetric Titration of Vitamin C11
advertisement

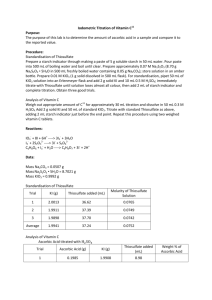
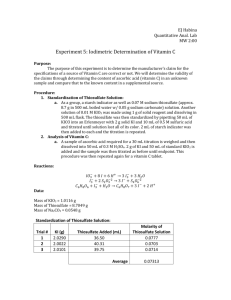
Orlando 1 Quantitative Analytical Chemistry Joseph Orlando Lab #5: Iodimetric Titration of Vitamin 𝐂 𝟏𝟏 Purpose: In this experiment we first standardized thiosulfate to use to determine the amount of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) present in a supplemental source. We compared the experimental data to the manufacturer’s specifications to see if they were met. IO3- + 8 I + 6 H+ -----> 3 I- + 3 H2O I3- + 2 S2O32- -----> 3 I- + S4O62C6H8O6 + I3- -----> C6H8O7 + 3 I- + 2 H+ Procedure: Standardization of Thiosulfate Solution 1. Prepare starch indicator; make a paste of 5g soluble starch in 50mL H2O then pour the paste into 500mL boiling H2O, boil until clear. 2. Prepare 0.07M Na2S2O3 by dissolving ~8.7g Na2S2O3 in 500mL freshly boiled H2O containing 0.05g of Na2CO3. Store in tightly capped amber bottle. Prepare 0.01M KIO3 by weighing ~1g solid reagent and dissolving in 500mL flask. 3. Standardize thiosulfate solution. Pipet 50mL KIO3 solution into an Erlenmeyer flask. Add 2g solid KI + 10mL 0.5M H2SO4. Titrate with thiosulfate until solution becomes pale yellow. Add 2mL starch solution and complete titration. Repeat this process three times. Analysis of Vitamin C 1. Weigh vitamin C for a ~30mL titration and dissolve in 50mL 0.3M H2SO4. 2. Add 2g solid KI and 50mL standard KIO3. Titrate with standard thiosulfate as above, add 2mL starch before endpoint. Repeat using two weighed vitamin C tablets. 3. Determine wt% of vitamin C in tablet and report standard deviation and accuracy of titrations. Orlando 2 Data: Standardization of Thiosulfate Solution KI(g) Thiosulfate added(mL) Trial 1 2.0581 0 Molarity of Thiosulfate Solution 0 Trial 2 2.0405 39.52 0.072M Trial 3 2.0020 38.45 0.074M Average 2.0335 38.98 0.073M Standard Deviation 0.0014 Ascorbic Acid Titration Trial 1 KI(g) Ascorbic Acid(g) 2.0003 0.1998 Thiosulfate added(mL) 9.29 Weight % of Ascorbic Acid 27.03% Weight % of Vitamin C 72.53% Vitamin C Titration Vitamin C(g) KI(g) Trial 1 0.2645 1.9998 Thiosulfate added(mL) 8.79 Trial 2 0.3142 2.0038 15.62 75.89% Average 0.2894 2.0018 12.21 74.21% Standard Deviation 2.376 Equations: 𝑴𝒐𝒍𝒂𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒚 𝒐𝒇 𝑲𝑰𝑶𝟑 = 1.0183𝑔 𝐾𝐼𝑂3 𝑥 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 1 𝑥 = 0.0095𝑀 214 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑠 0.5 𝐿 Orlando 3 𝑴𝒐𝒍𝒂𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒚 𝒐𝒇 𝑵𝒂𝟐 𝑺𝟐 𝑶𝟑 = 0.0095𝑀 𝐼𝑂3− 𝑥 0.05 𝐿 𝑥 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼 − 2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑆2 𝑂3 1 −𝑥 − 𝑥 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼𝑂3 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3 0.03952𝐿 = 0.072𝑀 𝑨𝒎𝒐𝒖𝒏𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝑨𝒔𝒄𝒐𝒓𝒃𝒊𝒄 𝑨𝒄𝒊𝒅 𝑵𝒆𝒆𝒅𝒆𝒅 = 0.0095𝑀 𝐼𝑂3− 𝑥 0.05𝐿 𝑥 0.073𝑀 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 𝑥 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− = 0.001425 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 0.03𝐿 = 0.001095 mol 𝐼3− 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 2 0.00141 − 0.001095 = 0.000306 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐼3− 𝑾𝒆𝒊𝒈𝒉𝒕 𝑷𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝑨𝒔𝒄𝒐𝒓𝒃𝒊𝒄 𝑨𝒄𝒊𝒅 = 0.00929𝐿 𝑥 0.073𝑀 1 mol S2 O3 1 mol I3 3.39 10 4 excess I3 1 mol Na 2 S 2 O3 2 mol S2 O 2 Grams of Ascorbic Acid (Calculated) mol of I3− × 1 mol A. A. molar mass A. A × = grams of A. A 1 mol I3− 1 mol Percent Yield of Ascorbic Acid Grams calculated × 100 = % A. A. Grams started with Conclusion: The purpose of this experiment was to determine whether the amount of Vitamin C in a store bought tablet matched or exceeded the amount of Vitamin C that was claimed to be in the tablet by the manufacturer. The calculated weight percent of vitamin C in the tablets was 74.21%±2.376. Some product was most likely lost during transfer which would lower the weight percent. The calculated weight percent of vitamin C seems to be very close to the manufacturers claim. Post Lab Questions: 1. What was the undissolved solid from the tablets? The undissolved solid from the tablets was calcium carbonate. 2. Did the amount of vitamin C in the tablet meet or exceed the manufacturer’s claim? The amount of vitamin C experimentally calculated was an average of 74.21% and somewhat met the manufacturers claims although it did not exceed their claims. Human error caused by transferring of the product may have caused this discrepancy in data.