File
advertisement
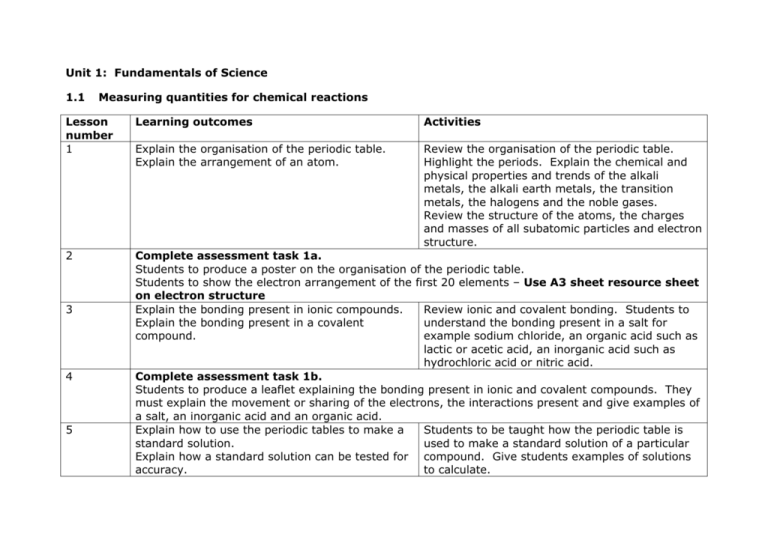
Unit 1: Fundamentals of Science 1.1 Measuring quantities for chemical reactions Lesson number 1 Learning outcomes Activities Explain the organisation of the periodic table. Explain the arrangement of an atom. Review the organisation of the periodic table. Highlight the periods. Explain the chemical and physical properties and trends of the alkali metals, the alkali earth metals, the transition metals, the halogens and the noble gases. Review the structure of the atoms, the charges and masses of all subatomic particles and electron structure. 2 Complete assessment task 1a. Students to produce a poster on the organisation of the periodic table. Students to show the electron arrangement of the first 20 elements – Use A3 sheet resource sheet on electron structure Explain the bonding present in ionic compounds. Review ionic and covalent bonding. Students to Explain the bonding present in a covalent understand the bonding present in a salt for compound. example sodium chloride, an organic acid such as lactic or acetic acid, an inorganic acid such as hydrochloric acid or nitric acid. Complete assessment task 1b. Students to produce a leaflet explaining the bonding present in ionic and covalent compounds. They must explain the movement or sharing of the electrons, the interactions present and give examples of a salt, an inorganic acid and an organic acid. Explain how to use the periodic tables to make a Students to be taught how the periodic table is standard solution. used to make a standard solution of a particular Explain how a standard solution can be tested for compound. Give students examples of solutions accuracy. to calculate. 3 4 5 Explain how to perform a titration. 6 7 8 9 Demonstrate how to perform a titration so that students will be able to complete the activity next lesson. Explain to students how titrations can be used to assess the accuracy of a standard solution. Work through some examples with the students. Complete assessment activities 2a and 2b Students are to prepare a 100ml 1Mol sodium hydroxide solution and a 100ml 2Mol sodium hydrogen sulphate solution. Complete the observation sheet on standard solution Students to titrate 25ml of their sodium hydroxide against a known concentration of hydrochloric acid using phenolphalein as an indicator. Students to repeat the investigation 3 times to calculate the mean. Students to titrate their sodium hydrogen sulphate solution against a known concentration of sodium hydroxide using phenolphalein as an indicator. They are to repeat 3 times to calculate a mean. Complete the observation sheet on performing a titration. Complete assessment activities 2a and 2b Students to write a report on how they made their standard solutions, highlighting the importance of using the periodic table in the calculations. They are then to explain how they assessed the accuracy of their prepared solutions. Explain how they produce standard solutions and Allow students to carry out research as to how assess their accuracy in industry standard solutions are carried out in industry and how they are different to the procedures that they have carried out. Explain how standard solutions are assessed for their accuracy in industry. Students to complete assessment activity 3. Write a report on how standard solutions are prepared and tested for their accuracy in industry and how these procedures differ from that done in the school laboratory.