winds upper
advertisement
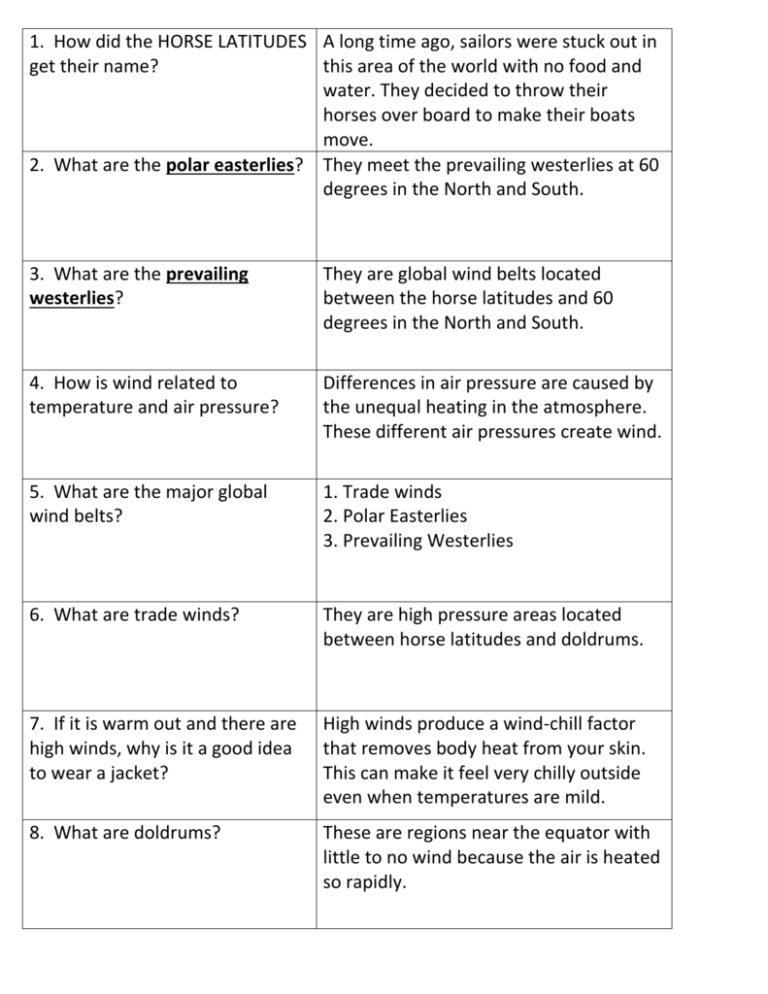
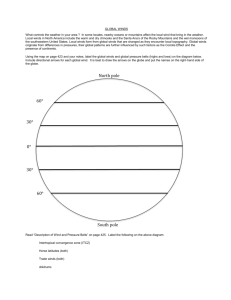
1. How did the HORSE LATITUDES A long time ago, sailors were stuck out in get their name? this area of the world with no food and water. They decided to throw their horses over board to make their boats move. 2. What are the polar easterlies? They meet the prevailing westerlies at 60 degrees in the North and South. 3. What are the prevailing westerlies? They are global wind belts located between the horse latitudes and 60 degrees in the North and South. 4. How is wind related to temperature and air pressure? Differences in air pressure are caused by the unequal heating in the atmosphere. These different air pressures create wind. 5. What are the major global wind belts? 1. Trade winds 2. Polar Easterlies 3. Prevailing Westerlies 6. What are trade winds? They are high pressure areas located between horse latitudes and doldrums. 7. If it is warm out and there are high winds, why is it a good idea to wear a jacket? High winds produce a wind-chill factor that removes body heat from your skin. This can make it feel very chilly outside even when temperatures are mild. 8. What are doldrums? These are regions near the equator with little to no wind because the air is heated so rapidly. 9. What are horse latitudes? These areas of CALM air are found at 30 degrees north and 30 degrees south. 10. What are jet streams? They are very wide, shallow bands of high speed winds in the upper troposphere. These winds circle the globe at 200-400 km per hour. 11. What are local winds? Winds that blow over short distances. 12. What is wind? It is the horizontal movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. 13. What is the Coriolis Effect? It is the way Earth’s rotation makes winds curve. 14. What is a global wind? Winds that blow steadily and in specific directions over long distances. 15. What is a land breeze? It occurs at night and is a result of the land’s ability to cool off faster than water. The wind blows from the denser, cooler air over the land toward the less dense, warmer air over the sea. It is the flow of air from land to a body of water. It is the result of the land’s ability to warm up faster than water. The wind blows from the more dense, cooler air over the sea toward the less dense, warmer air over the land. It also is a local 16. What is a sea breeze? wind that blows from an ocean or a lake. 17. What are winds described by? Direction and Speed 18. What causes global winds? They are caused by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface over a large area. 19. What causes local winds? Unequal heating of Earth’s surface within a small area. 20. What do you use to measure Wind? anemometer 21. What happens to the northern winds because of the Coriolis Effect? They gradually turn toward the right. The increased cooling a wind can cause. 22. What is the wind-chill factor? 23. Which way do winds curve in They gradually turn toward the left. the southern hemisphere because of the Coriolis Effect?