Periodic Table Study Guide
advertisement

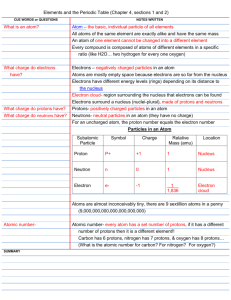
INVESTIGATIVE SCIENCE NAME_________________ PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS STUDY GUIDE PRD.___DATE___________ VOCABULARY TO KNOW: (Define each or draw a picture!) PLEASE BE DETAILED! Elements Chemical Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass Periodic Table Periods of the Periodic Table Groups of the Periodic Table Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Metals Non-metals Metalloids Noble Gases Halogens Transition Metals (Lanthanides & Actinides) Physical Properties Chemical Properties Isotopes Label the following diagram from the periodic table using these terms: Chemical symbol, chemical name, atomic number, atomic mass Fill in the following table with information about each type of subatomic particle: Subatomic Particle: Protons Location in the Atom: Charge (+, -, No charge) Mass Neutrons Electrons What does the Solubility Test determine about a substance? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ The following table gives the results of a series of tests done to identify different substances. Substance Solubility Test Iodine Test PHTH Test Cornstarch Epsom salt Baking Soda Table Salt Insoluble Soluble Soluble Soluble + - Do Not Test + - Acetic Acid Test + - NaOH Test Do Not Test + - A chemist was testing an unknown substance and determined it had the following characteristics: Soluble in water, Iodine and NaOH tests were negative, PHTH and Acetic Acid were positive. What chemical was the chemist testing? _________________ IMPORTANT SCIENTISTS TO KNOW: Know what contribution to the development of the periodic table that each of these scientists made: 1. 2. 3. 4. Lavoisier, 1789: Mendeleev, 1869: Moseley, 1913: Seaborg, 1945: Identify the following diagrams. Write the name of the scientist who made these early attempts at a periodic table: This table contained the 63 elements that had been discovered at the time. It also left “blanks” where undiscovered elements would be placed. Whose table was this? This Table of Simple Elements had 32 substances. Some were not elements, but were compounds or mixtures. It even contained heat and light as elements. Whose table was this? The modern periodic table was described by this scientist. His revision of the periodic table reflected the new information discovered about quantum mechanics. He also separated the lanthanides and actinides into their own block. Whose table was this? This scientist demonstrated that elements are unique based on the number of protons in the atom. His periodic table was the first to organize the elements by atomic number (the number of protons). Whose table was this? For the following diagram, label and color all of the following groups: Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Metals, Metalloids, Non-metals, Halogens, Noble Gases, Lanthanides, Actinides Key: ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ A neutral atom contains the same number of protons and electrons. An ion is an atom that _____________________________________. Isotopes are atoms that _________________________________________________. The following describes different kinds of atoms. There is one that is a neutral atom, one that is an isotope, and one that is an ion. Each of the following shows a square from the periodic table for a particular element. Read a description of the atom and answer the questions. This atom has 11 protons, 12 neutrons and 10 electrons. What element is this? _______ Is this atom neutral, an ion or an isotope? ________________ This atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. What element is this? ____________ Is this atom neutral, an ion or an isotope? ________________ This atom has 6 protons, 8 neutrons and 6 electrons. What element is this? ____________ Is this atom neutral, an ion, or an isotope? _______________ Know how to draw an electron shell diagram, following the rules. Draw the following elements: Oxygen, Neon, Aluminum and Potassium. Know how to draw a Lewis structure. Draw the Lewis structure for: Argon, Arsenic, and Rubidium Define the following terms: Know the general trend on the periodic table for each: 1. Atomic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity