5 zone sequence - My Anatomy Mentor
advertisement

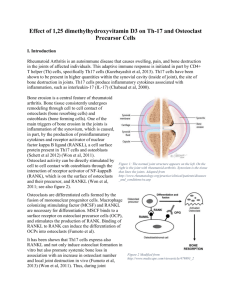
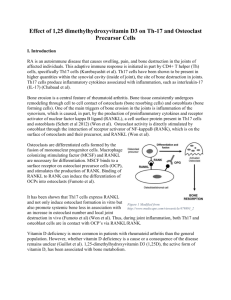
What’s happening in each zone recap? 1. Resting zone is an anchor for the rest of the epiphyseal region. Randomly dispersed chondrocytes in lacunae. The youngest tissue, which will converted to trabeculae? 2. Proliferation (growth) zone is the mitotic zone (abuts resting zone) Cells form into stacks Younger cells at the top where cell maturation occurs older cells begin to divide pushing epiphysis away from the diaphysis long bone lengthens 3. Hypertrophy (enlarge) (where cells eventually die) Older chondrocyte cells closest to diaphysis enlarge Lacunae erode and enlarge Alkaline phosphatate (which helps with calcification) released here but not active till next zone 4. Erosion (calcification) Osteoclast and osteoblast most active here acting together (3rd location where these 2 work together). Osteoclast punching holes in matrix while osteoblast lays down new bone Alkaline phosphate speeds up calcification 5. Diaphysis (ossification) Bone being pushed into ossification zone as a result of osteoblast and osteoclast above Osteoblast and osteoclast both active here too Process of deposition and resorption occurring on outer edges of compact bone layer Remodeling occurring Hematopoiesis blood cell formation produced here (especially in neck & head of femur). This is where red marrow is layed down. This is a primary area for stem cells to be taken from (stem cells in the form of hemocytoblast cells, which is what is laying down the blood itself)