Overall Objective Objectives Activities Assessments Materials

Overall
Objective
Outcome:
MS7.1
Investigate the properties and applications of solutions, including solubility and concentration.
Objectives Activities Assessments Materials
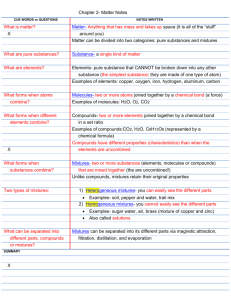
Construct a graphic organizer for the classification of matter that includes mixtures, pure substances, elements, compounds, mechanical mixtures, and solutions.
Classify common substances (e.g.,
Kool-Aid, vinegar, bubble bath, soft drinks, juice, chocolate chip cookies, salad dressings, hand lotion, shampoos, tea, bread, soil, and concrete) as pure substances, mechanical mixtures, or solutions.
Construct a graphic organizer for the classification of matter that includes mixtures, pure substances, elements, compounds, mechanical mixtures, and solutions
Describe the characteristics of pure substances, mechanical mixtures, and solutions.
-start off by making a title page for the unit
-read an article and try to pick out words important to the unit (in groups)
- make a graphic organizer to keep definitions for the unit
-introduce the weekly learning log
-demo correct microscope use
-have students fill in microscope names
-students will complete a mini lab with the microscope
-Begin by reviewing lab safety procedures and introducing
WHMIS
-Have students take home the
WHMIS worksheet and fill it in for homework
-Have students complete the heterogenous/ homogenous lab using microscopes
-movitational set- looking for a solution lab, have students predict what will happen
-students will write notes on classifying matter and will add mechanical mixture, element and compound to their definition page
-students will then go to the side table and classify common objects into the proper category (pure, mixture, etc)
-students will then perform the lab floating colors and hand in to assess for learning
-if time go through common substances and give students the correct answers
- checklist for completeness
-informal- check and correct microscope lab
-formal mark labs
-assess for learning, checkpoint to ensure outcomes obtained
- table for the graphic organizer
-article to be read in groups
-microscopes
-newspaper
-slides
-handouts
-microscope
-magnifying glasses
-milk
-o.j
-7-up
-common substances to be categorized
-tust tubes, food colouring, oil
Listen to and consider the ideas of classmates when classifying materials as pure substances or mixtures.
Create mechanical mixtures and solutions using common materials and compare the physical properties of the original materials and the resultant mixture or solution.
If at Christmas time, make borax crystal ornaments and have stds describe the properties of the solution before and after
Examine a variety of objects and materials, and record qualitative
(e.g., colour, texture, and state of matter) and quantitative (e.g., density, melting point, and freezing point) physical properties of those objects in a chart or data table
-mystery cookie lab
Examine a variety of objects and materials, and record qualitative
(e.g., colour, texture, and state of matter) and quantitative (e.g., density, melting point, and freezing point) physical properties of those objects in a chart or data table
Create mechanical mixtures and solutions using common materials and compare the physical properties of the original materials and the resultant mixture
Mix it up lab (may take longer than one period
None -borax
-beakers
-hot plates
-pipe cleaners
Informal- write a paragraph describing the properties of the substances, which powder was the cookie mix and why?
-flour
-icing sugar
-baking powder
-baking soda
-corn starch
-sugar cookies/juice for after lab
Formal- use rubric to assess lab report
-test tubes
-water
-antacid tablets
-Pepper
-salt
-sugar
-flour
Test tube stoppers
Outcome:
MS7-2-
Investigate methods of separating the components of mechanical mixtures and solutions, and analyze the impact of industrial and agricultural applications of those methods or solution.
State the four main ideas of the particle model of matter
Create models and/or physical representations that depict the nature of particles in pure substances, mechanical mixtures, and solutions according to the particle model of matter.
-mot. Set- what’s the total volume?
-notes on the particle theory of matter
-activity mixing it up again
Formal: exit slip- Relate the mot. Set to the activity results
-what did you learn today?
-How well did you know this before this lesson?
-marbles
-sand
-beaker
-alcohol
-water
-graduated cylinders
Describe methods used to separate the components of mechanical mixtures and solutions, including mechanical sorting, filtration, evaporation, distillation, magnetism, and chromatography.
Describe common household examples of technologies that are used to separate components of mechanical mixtures or solutions (e.g., kitchen strainer, oil and air filters).
Design and conduct an experiment to determine the effectiveness and/or efficiency of one or more methods of separating mechanical
Outcome:
MS7.3
Investigate the properties and applications of solutions, including solubility and concentration.
mixtures and solutions.
Provide examples of solid, liquid, and gaseous solutions and identify which substance is the solute and which is the solvent in each solution.
Describe the characteristics of solutions using the terms solute, solvent, soluble, and insoluble, based on the particle model of matter.
Create and describe the concentration of student-prepared dilute, concentrated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions using those qualitative terms and quantitative measurements
(e.g., parts per million [ppm], g/L, and g/100 mL).
Investigate the factors that determine how quickly a solute dissolves in a solvent.
Analyze the effects of technological inventions or processes related to solutions (e.g., water softeners, water treatment plants, solution
mining, agricultural sprays, insecticides, bleaches, and drain cleaners) on self, community, and the environment.