Pure Substances and Mixtures
advertisement

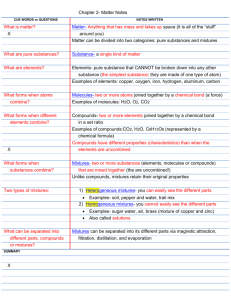
Pure Substances, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures What are pure substances? PURE SUBSTANCES Substances made of one kind of material with a unique set of chemical and physical properties. Elements and compounds are pure substances. What is an element? ELEMENT a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances There are slightly more than 100 known chemical elements that are arranged on the periodic table developed by Dimitri Mendelev. Each element is abbreviated with one or two symbols. The 1st letter is capitalized and the 2nd is not. Each symbol represents the English name, old name, or Latin name of the element. EXAMPLE: (Latin) Aurum-Gold –Au (English) Oxygen – O (Old) Natrium – Sodium - Na Some elements are named after famous scientists, countries, states, and planets. (101) Mendelevium – scientist (32) Germanium – Germany (98) Californium – California (92) Uranium Uranus What are compounds? COMPOUNDS 2 or more elements chemically combined EX: magnesium oxide (MgO2) Magnesium Oxygen Separating Compounds Compounds can be separated by chemical means because they are chemically combined. Compounds can be broken down by electrolysis. Electrolysis literally means “to tear apart with electricity”. It is a technique using an electric current to pass through a substance. If the substance is a compound, it may be broken down into the separate elements that form it. EX: H2O (water) If an electric current passes through the compound, the compound will break down into the two elements hydrogen and oxygen. What is a mixture? MIXTURES a blend of two or more pure substances Types of Mixtures Heterogeneous Mixture a mixture that has visibly different parts Homogeneous Mixture mixtures that do not contain visibly different parts (Hetero- and Homo- are two Greek roots that mean “different” and “same”.) Heterogeneous vs Homogeneous Separating Mixtures Mixtures can be separated by: decantation, filtration, crystallization, distillation, chromatography. Decantation Decantation gentle pouring off of a liquid without disturbing a solid sediment EXAMPLE: *cleaning a fish tank and leaving behind most of the sand, shells, and plants * drinking coffee and leaving small residue of coffee grounds behind in a cup Filtration Filtration passage of a liquid or gas through a porous substance for the purpose of removing suspended solids. A mixture of water and an insoluble substance like sand can be separated by filtering. Crystallization Crystallization refers to the formation of solid crystals from a homogeneous solution. It is essentially used as a solid-liquid separation technique. Distillation Distillation the process in which a liquid is evaporated and the vapors condensed The solution is heated until it boils. The liquid with the lowest boiling point boils first and becomes a vapor (gas). The vapor is cooled in the condenser until the temperature falls below the boiling point when it condenses back into a liquid which is collected in a container. Chromatography Chromatography process used to separate mixtures using a solvent (water) that carries a solute (ink) up a strip of paper Heterogeneous mixtures can be separated by physical means such as filtration. Homogeneous mixtures can be separated by distillation, crystallization, & chromatography.