Earth`s Global Topography
advertisement

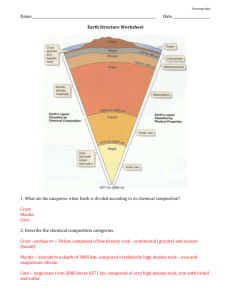
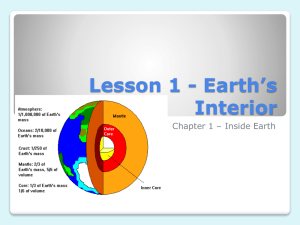
Earth's Global Topography Materials: Calculator, pencil. Other materials provided in lab. Basalt (Ocean crust) [1] As exactly as you can, weigh (grams) the sample of basalt (ocean crust). Add your data to the basalt density chart below. [2] Determine the volume (by water displacement, see Figure below) of the sample of basalt. Add your data to the basalt density chart below. [3] Calculate the density of your sample of basalt to tenths of a g/ cm3 [4] Determine the average density of basalt using all ten lines of sample data in the basalt density chart. Granite (Continental crust) [5] As exactly as you can, weigh (grams) the sample of granite (continental crust). Add your data to the granite density chart below. [6] Determine the volume (by water displacement, see Figure below) of the sample of granite. Add your data to the granite density chart below. [7] Add your data to the granite density chart below. Calculate the density of your sample of granite to tenths of a g/ cm3. [8] Then determine the average density of granite using all ten lines of sample data in the granite density chart. BASALT DENSITY CHART Basalt Sample Sample weight (g) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 40.5 29.5 46.6 31.5 37.6 34.3 78.3 28.2 55.6 Sample Volume (cm3) 13 10 15 10 12 11 25 9 18 Average density of basalt: ___________________________ Sample Density (g/ cm3) 3.1 3.0 3.0 3.2 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 GRANITE DENSITY CHART Granite Sample Sample weight (g) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 32.12 27.8 27.6 31.1 58.6 62.1 28.8 82.8 52.2 Sample Volume (cm3) 12 10 10 11 20 22 10 30 20 Sample Density (g/ cm3) 2.7 2.8 2.8 2.8 2.9 2.8 2.9 2.8 2.6 Average density of granite: ____________________________ Seismology (the study of Earth's structure and composition using earthquake waves), and mantle xenoliths indicate that the upper mantle is peridotite rock. The peridotite has an average density of about 3.3 g / cm3 and is capable of slow flow. [1] The average thickness of basaltic ocean crust is 5.0 km. Use your average density of basalt to calculate how high (in kilometers) basalt floats in the mantle. Show your work. Floating equation Depth of crust that sinks: (density of crust/density of mantle) x crust thickness = depth of crust that sinks Depth of crust that floats: crust thickness – depth of the crust that sinks = depth of crust that floats [2] The average thickness of granitic continental crust is 30.0 kilometers. Use the average density of granite and your floating equation to calculate how high (in kilometers) granite floats in the mantle. Show your work. [3] What is the difference (in km) between your answers in l and 2? Reflect on all of your work in this laboratory. Explain why Earth has a bimodal global topography Procedure for determining volume of a rock sample by water displacement. A. Place water in the bottom of a graduated cylinder. Choose a graduated cylinder into which the rock will fit easily and add enough water to be able to totally immerse the rock. It is also helpful to use a dropper or wash bottle and bring the volume of water (before adding the rock) up to an exact graduation mark like the 5.0 ml mark. Record this starting volume of water. B. Carefully slide the rock sample down into the same graduated cylinder and record this ending level of the water (7.8 ml mark). Subtract the starting volume of water from the ending volume of water to obtain the displaced volume of water (2.8 ml, which is the same as 2.8 cm3). This volume of displaced water is also the volume of the rock sample.