Multiplication and Division_Year 5 32KB May 06 2015
advertisement

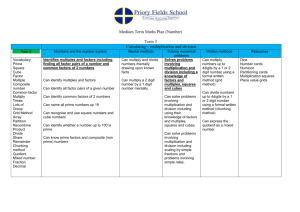
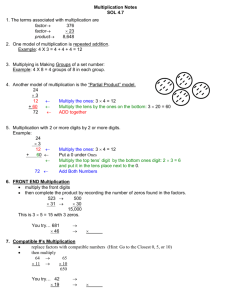
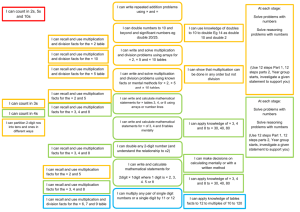
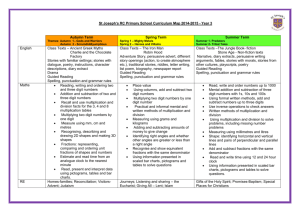
Multiplication and Division Year 5 I can multiply a two digit number by a two digit number I can multiply a four digit number by a one digit number I can multiply a three digit number by a two digit number I can multiply a number with 1 decimal place by a single digit I can divide a four digit number by a one digit number I can divide a three digit number by a two digit number Group 1 Problem solving and Reasoning Group 2 Problem solving and Reasoning Group 3 Problem solving and Reasoning Group 4 Problem solving and Reasoning Multiplication and Division Aims of the National Curriculum Identify multiples and factors, including finding all factor pairs of a number, and common factors of two numbers become fluent in the fundamentals of mathematics, including through varied and frequent practice with increasingly complex problems over time, so that pupils have conceptual understanding and are able to recall and apply their knowledge rapidly and accurately to problems Know and use the vocabulary of prime numbers, prime factors and composite (non-prime) numbers Establish whether a number up to 100 is prime and recall prime numbers up to 19 Recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers, and the notation for squared (2) and cubed (3) Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts Multiply and divide whole numbers and those involving decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a one- or two-digit number using a formal written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit number using the formal written method of short division and interpret remainders appropriately for the context Solve problems involving multiplication and division including using their knowledge of factors and multiples, squares and cubes Solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division and a combination of these, including understanding the meaning of the equals sign © Tara Loughran Solve problems involving multiplication and division, including scaling by simple fractions and problems involving simple rates. reason mathematically by following a line of enquiry, conjecturing relationships and generalisations, and developing an argument, justification or proof using mathematical language can solve problems by applying their mathematics to a variety of routine and non-routine problems with increasing sophistication, including breaking down problems into a series of simpler steps and persevering in seeking solutions.