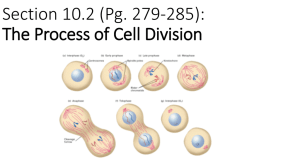
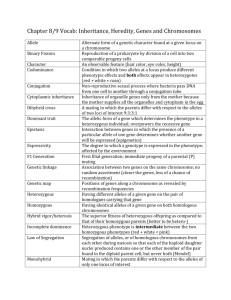
Biology Test Sister chromatids are attached to each other at an area
advertisement

Biology Test 1. Sister chromatids are attached to each other at an area called the: a.) b.) c.) d.) Centriole Centromere Spindle Chromosome 2. If a cell has 12 chromosmes, how many chromosomes will each of its daughter cells have after mitosis: a.) b.) c.) d.) 4 6 12 24 3. At the beginning of cell division, a chromosome consists of two: a.) b.) c.) d.) Centromeres Centrioles Chromatids Spindles 4. The phase of mitosis during which chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate from one another is: a.) Prophase b.) Anaphase c.) Metaphase d.) Telophase 5. The timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells is believed to be controlled by a group of closely related proteins known as: a.) b.) c.) d.) Chromatids Cyclins Centromeres Centrioles 6. In the cell cycle, external regulators direct cells to: a.) b.) c.) d.) Speed up or slow down the cell cycle Remain unchanged Proceed and then stop the cell cycle Grow uncontrollably 7. Uncontrolled cell division occurs in: a.) b.) c.) d.) Cancer Mitosis Cytokinesis Cyclin 8. Different forms of a gene are called: a.) b.) c.) d.) Hybrids Dominant factors Alleles Recessive factors 9. If a homozygous tall pea plant and a homozygous short pea plant are crossed: a.) b.) c.) d.) The recessive trait seems to disappear The offspring are of medium height No hybrids are produced All the offspring are short 10. A Punnett square is used to determine the: a.) b.) c.) d.) Probable outcome of a cross Actual outcome of a cross Result of mitosis Result of meiosis 11. Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be: a.) b.) c.) d.) Hybrid Heterozygous Homozygous Dominant 12. The physical characteristics of an organism are its: a.) b.) c.) d.) Genetics Heredity Phenotype Genotype 13. A situation in which a gene has more than two alleles is known as: a.) b.) c.) d.) Complete dominance Codominance Polygenic dominance Multiple alleles 14. Unlike mitosis, meiosis in male mammals results in the formation of: a.) b.) c.) d.) One haploid cell Three diploid polar bodies Four diploid gamete cells Four haploid gamete cells 15. To maintain the chromosome number of an organism, the gametes must: a.) b.) c.) d.) Become diploid Become recessive Be produced by mitosis Be produced by meiosis 16. A gene map shows: a.) b.) c.) d.) The number of possible alleles for a gene The relative locations of genes on a chromosome Where chromosomes are in a cell How crossing-over occurs 17. A nucleotide does NOT contain: a.) b.) c.) d.) A 5-carbon sugar Polymerase A nitrogen base A phosphate group 18. In prokaryotes, DNA molecules are located in the: a.) b.) c.) d.) Nucleus Ribosome Cytoplasm Histone 19. The main enzyme involved in linking individual nucleotides into DNA molecules is: a.) b.) c.) d.) Transfer RNA Ribose RNA polymerase DNA polymerase 20. The process by which the genetic code of DNA is copied into a strand of RNA is called: a.) b.) c.) d.) Translation Transcription Transformation Replication 21. In a messenger RNA, each codon specifies a particular: a.) b.) c.) d.) Nucleotide Purine Amino acid Pyrimidine 22. Changes in the DNA sequence that affect genetic information are known as: a.) Replications b.) Mutations c.) Transformations d.) Prokaryotes 23. A normal human diploid zygote contains: a.) b.) c.) d.) 23 chromosomes 46 chromosomes 44 chromosomes XXY chromosomes 24. Most sex-linked genes are found on the: a.) b.) c.) d.) Y chromosome O chromosome YY chromosome X chromosome 25. Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that is: a.) b.) c.) d.) Sex-linked Sex-influenced Fairly common More common in women than men 26. Which parental pair could produce females with colorblindness: a.) b.) c.) d.) Homozygous normal-vision mother, father with colorblindness Mother with colorblindness, normal-vision father Heterozygous normal-vision mother, normal-vision father Heterozygous normal-vision mother, father with colorblindness 27. A common genetic disorder characterized by bent and twisted red blood cells is: a.) Cystic fibrosis b.) Hemophilia c.) Sickle cell division d.) Muscular dystrophy 28. Which of the following techniques takes advantage of repeated DNA sequences that do not code for proteins: a.) DNA fingerprinting b.) DNA sequence c.) Genetic engineering d.) Rapid sequencing 29. The process of attempting to cure genetic disorders by placing copies of healthy genes into cells that lack them is known as: a.) b.) c.) d.) Gene therapy DNA fingerprinting Rapid sequencing The Human Genome Project 30. Which of the following is NOT a phase of mitosis: a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Prophase Interphase