Metamorphic Rocks
advertisement
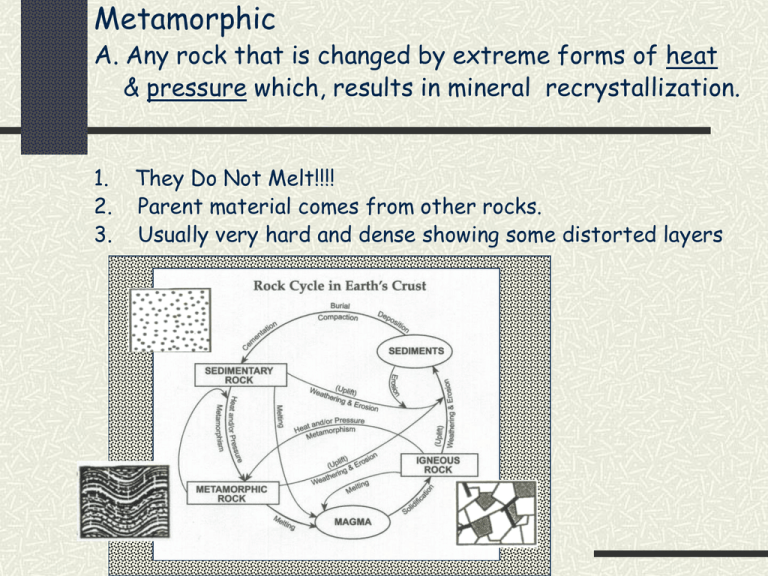
Metamorphic A. Any rock that is changed by extreme forms of heat & pressure which, results in mineral recrystallization. 1. 2. 3. They Do Not Melt!!!! Parent material comes from other rocks. Usually very hard and dense showing some distorted layers B. Metamorphics are classified by their texture & composition. Foliated Textures: “show distortion” Mineral Alignment: - The minerals are squished into flat layers - Schistocity: Low grade metamorphic pressure Ex. Slate, Phylite, Schist Banding: - Minerals are separated into different layers - Movement of crystals without melting - Seperated by mineral density differences - High grade metamorphism Ex. Gneiss Formation of Metamorphic Rocks Stage 1 Mineral Alignment Pressure x z z zY x x Y x Y z Y z x Heat x -Original parent rock with minerals in rock structure. (X,Y,Z). z - Rock is subject to low grade pressure & temperatures & then the minerals are flattened. Stage 2 Banding "Recrystallization" extreme heat & pressure allows individual crystals to… - Grow larger - Consolidate together - Separate according to density differences. x x z Y xz x x xz zz z x z x Y Y Yx z Y Yz z xY z Y Y x Y xzxx x x x x zz z zx xz zz z x z z Y YY YY Y Y Y YY C. Types of Metamorphic processes. 1. Contact: Occurs when molten rock (intrusion or extrusion) comes into contact with surrounding materials. - Intrusion will always be the younger rock - Heat is the primary agent for metamorphism. 2. Regional: Occurs over large areas under mountain ranges. Foliated Rocks Usually are derived from many mineral types. Phylite Schist Gneiss Increasing Depth, Pressure & Temperature Non-foliated Rocks Usually are derived from one mineral type. Quartzite Marble