Boiling point ( o C)
advertisement

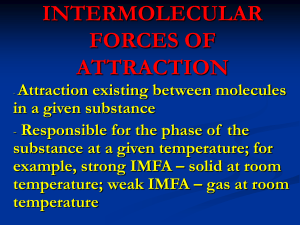
Worksheet 7 Bonding Review Intra- molecular bonding means bonding ___________ atoms Inter- molecular bonding means bonding ___________ molecules There are ______ types of Intra- molecular bonding _____________________ This type of bonding occurs between ______-_________ atoms. It involves atoms sharing ___________ to gain _____ valance _______ or a full _________. There are ______ elements which do this. They are known as the ___________ elements. They are; There are two types of ___________ compounds; ____________ molecular ____________ network. Name:__________________________ _______________________ compounds have low ___________ points and boiling _________. They ____________ conduct electricity and are generally ________________ in water. _____________________ compounds have _________ melting _______ and ___________ points. They __________ conduct electricity and are generally ________________ in water. ______________________ This type of bonding occurs between oppositely charged ________. It occurs when there is a _____________ difference in electronegativity. __________ compounds have a _____________ structure. They tend to have __________ melting and ___________ points, are ___________ in water and ______________ conduct electricity when molten or ________________. _____________________ This type of bonding occurs between _____________ atoms. It involves _______________ ions and ________________ electrons. It is due to the presence of these _____________ electrons that ___________ will _____________ electricity, are ___________ and ______________. _____________ is the only liquid __________ and one of only __________ liquid elements. There are ______ types of Inter- molecular bonding _____________________ This type of ______________ occurs when there is a ______________ separation of ___________ which arises when there is momentarily more _______________ on one side of the ___________ than the other. __________________________ accounts for why the ________________ can exist as liquids and solids at low temperatures. ____________________ This type of _______________ occurs when there is a ______________ in _________________ between two atoms in a molecule. It results in a __________________ dipole. _________________ This type of ________________ is a special type of ________________________that occurs when ______________ is directly bonded to an extremely ___________________ element such as ___________, _____________, or _____________. It is due to _____________________ that water has such a ___________ melting point. Questions 1. What is an ionic bond? 2. Why is sodium chloride neutral? 3. Explain what is meant by the term ‘electronegativity’. 4. Why are some covalent bonds between two atoms polar? 5. What is a dipole? 6. What types of molecules have permanent dipole- dipole forces? 7. Which of the substances listed below form hydrogen bonds between their molecules? Water (H2O) sodium chloride (NaCl) methane (CH4) ammonia (NH3) 8. What is another name for Van der Waals? hydrogen (H2) hydrogen fluoride (HF) 9. The table below shows the boiling points and molecular masses of some of the halogens. Substance Fluorine (F2) Chlorine (Cl2) Bromine (Br2) Iodine (I2) Molar Mass (g) 38 70 160 254 Boiling point (oC) -188.2 3.9 59 185.3 a) Describe the trend in boiling points b) Explain why this trend exists. 10. Why are the halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? Explain your answer. 11. Describe a metallic bond. 12. Explain why calcium will form a Ca2+ ion but not a Ca3+ ion. 13. Chromium a transition metal will form both the Cr2+ and Cr3+ ions. Write the formulas for the ionic compounds formed when each of these ions reacts with fluorine. 14. An external force easily deforms sodium metal, while sodium chloride shatters when the same amount of force is applied. Why do these two solids behave so differently? 15. Predict which solid in each of the following will have the higher melting point. a) NaCl or CsCl b) Ag or Cu c) Na2O or MgO 16. Explain why the term delocalized is an appropriate term for the electrons involved in metallic bonding. 17. A mercury atom drops from 1.413x10-18J to 1.069x10-18J. a) What is the energy of the photon emitted by the mercury atom? b) What is the frequency of the photon emitted by the mercury atom? c) What is the wavelength of the photon emitted by the mercury atom?