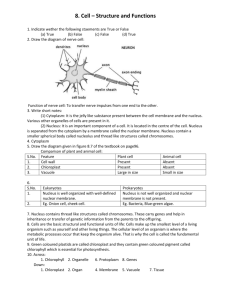
Name Period ______ Date ______ Ch. 3 – Cells Notes – part 1 Lab
advertisement

Name _____________________________________________ Period ____________ Date ____________ Ch. 3 – Cells Notes – part 1 Lab 4 – Care and Use of the Microscope Cells ___________________________ – the study of cells Cells vary greatly in _________________ and ______________________ Cells have two main parts – nucleus and cytoplasm Enclosed in a cell membrane (also called _______________________ membrane) Cell Characteristics Extremely _______________________________ Outpouchings and infoldings Porous ________________________________________ = controls what enters and leaves the cell. It allows some things to pass, but not others This is the MAIN FUNCTION of the ________________________________________ Cytoplasm Cytoplasm – the area between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. Where most ______________________________ reactions / activities take place Filled with a clear fluid called _____________________________ Contains many structures called organelles Organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – complex system of internal membranes, canals, or channels. Function = ___________________________________________ _____________________ ER – where ribosomes are located, protein manufacture _____________________ER – no ribosomes, lipid synthesis Golgi Apparatus (Bodies) – series of flattened, membranous sacs near the nucleus Function = _________________________________________________ Mitochondria – usually numerous, double layer membrane Function = Chemical energy transformed into _________________ (adenosine triphosphate) through the process of ___________________________________ Lysosomes – variable in size and shape Function = digestion and ___________________________ of foreign particles, microorganisms, and damaged or worn out cells and ___________________________________ Centrosome – composed of numerous microtubules Function = forms ________________________________ during cell division Vesicles – small sacs Function = ______________________________________________ Microfilaments & Microtubules – threadlike structures Function = cell __________________________ and cell _________________________________ Nucleus – large sphere usually in the center of the cell Function = __________________ the activities of the cell, contains _____________ information Nucleolus – small, dense structure within the nucleus Function = __________________________________________ Chromatin – loosely coiled “fibers” in nucleus, composed mainly of DNA and protein Function = contains information for ___________________________________________ Label the cell parts Lab 5 – Cell Structure and Function Cell Project Assignment Ch. 3 – Cellular Transport Notes – part 2 Passive Transport _____________________ – molecules move spontaneously (no energy used) from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Facilitated diffusion – molecules diffuse through a membrane through a_________. (no energy) Osmosis – the diffusion of ____________________ through a selectively permeable membrane Osmotic pressure = pressure to stop osmosis _______________ – molecules are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure Active Transport Molecules are moved against the concentration gradient. Requires the use of cellular ________________________ ____________________________ – transport of particles out of the cell ___________________________ – transport of particle into the cell Pinocytosis – liquids taken in Phagocytosis – solids taken in Solutions Solute – Substance ______________________ ________________________ – Substance in which a solute is dissolved (usually water) ______________________Solution – concentration of solute particles is greater outside the cell Causes water to go ______________ of cell _______________________Solution – concentration of solute particles is lower outside the cell Ex. Sugar (solute) dissolved in water (solvent) Causes water to __________________the cell __________________ Solution – concentration of solute particles is the same inside and outside Cause water movement to be ________________________ Gummi Bear Diffusion Lab Ch. 3 – Cell Cycle Notes – part 3 Life Cycle of a Cell Interphase Mitosis Cytoplasmic Division Differentiation Interphase Cell is in a resting state, ___________________ occurs, DNA ______________________ itself, cell _______________________________ Composed of 3 stages G1 S G2 Mitosis ______________________ Division Composed of 4 stages Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mnemonic = the dog peed on the mat (_________________________) Prophase Chromatin condenses and becomes visible as ________________________________ Spindle forms and centrioles migrate to the poles Nuclear membrane _________________________ Metaphase Chromosomes line up along the ________________________ Remember: Meta = middle Anaphase Individual ______________________ separate Telophase Nuclear membrane __________________________ Spindle disappears Cytokinesis The ______________________ (and hence the whole cell) separates Some still consider cytokinesis to be a part of mitosis…it is now a separate part of the cell cycle Differentiation When a stem cell starts to become a ____________________cell (like a muscle cell or nerve cell) Cell Cycle Game http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/2001/ Cell Cycle Project