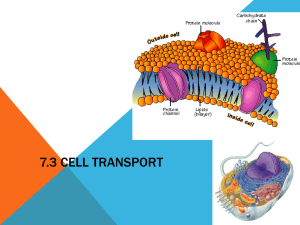
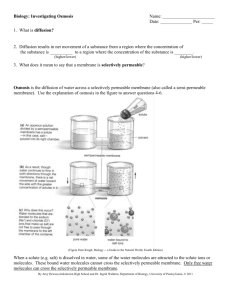
Definitions
advertisement
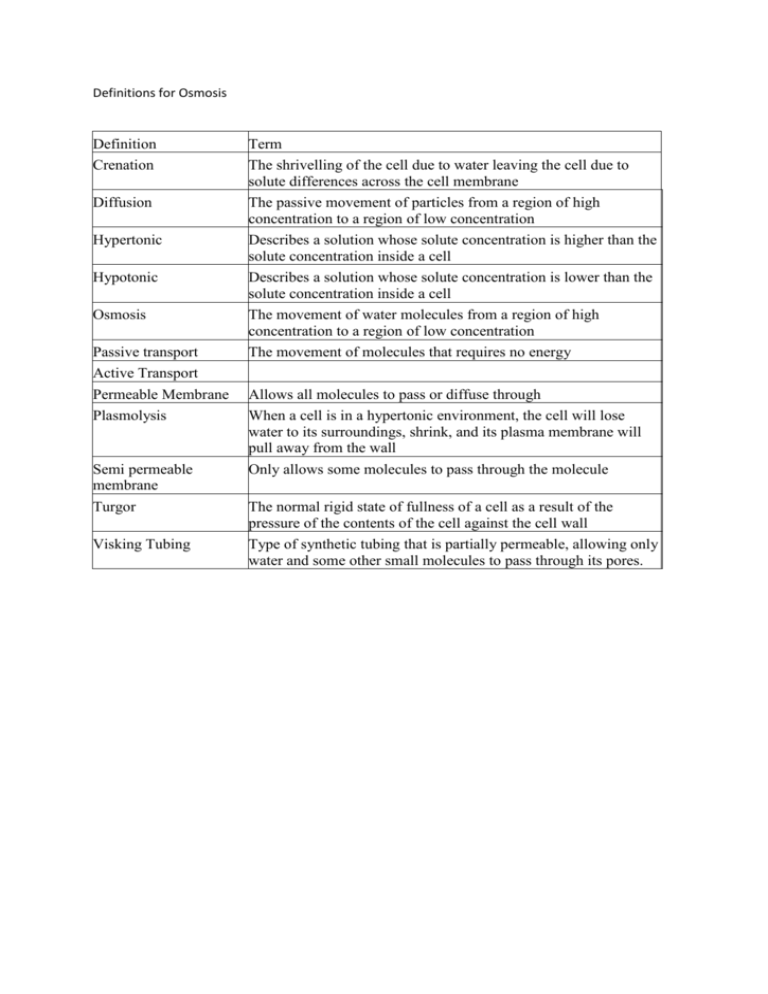
Definitions for Osmosis Definition Crenation Diffusion Hypertonic Hypotonic Osmosis Passive transport Active Transport Permeable Membrane Plasmolysis Semi permeable membrane Turgor Visking Tubing Term The shrivelling of the cell due to water leaving the cell due to solute differences across the cell membrane The passive movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration Describes a solution whose solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration inside a cell Describes a solution whose solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside a cell The movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration The movement of molecules that requires no energy Allows all molecules to pass or diffuse through When a cell is in a hypertonic environment, the cell will lose water to its surroundings, shrink, and its plasma membrane will pull away from the wall Only allows some molecules to pass through the molecule The normal rigid state of fullness of a cell as a result of the pressure of the contents of the cell against the cell wall Type of synthetic tubing that is partially permeable, allowing only water and some other small molecules to pass through its pores. Definition Crenation Diffusion Hypertonic Hypotonic Osmosis Passive transport Active Transport Permeable Membrane Plasmolysis Semi permeable membrane Turgor Visking Tubing Term Definition Term The shrivelling of the cell due to water leaving the cell due to solute differences across the cell membrane The passive movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration Describes a solution whose solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration inside a cell Describes a solution whose solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside a cell The movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration The movement of molecules that requires no energy Allows all molecules to pass or diffuse through When a cell is in a hypertonic environment, the cell will lose water to its surroundings, shrink, and its plasma membrane will pull away from the wall Only allows some molecules to pass through the molecule The normal rigid state of fullness of a cell as a result of the pressure of the contents of the cell against the cell wall Type of synthetic tubing that is partially permeable, allowing only water and some other small molecules to pass through its pores.