Bio_246_Lab_files/Lab 6 Anatomy of leg and foot
advertisement

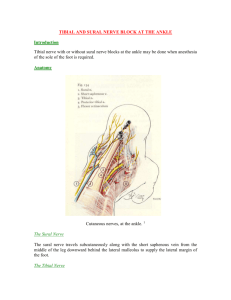
Lab 6 Anatomy of leg and foot. The tibia is the major weight-bearing bone in the leg. Move your hands anterior and inferior to a prominent bump called the tibial tuberosity. It is just inferior to the patella and acts as a common attachment for the quadriceps femoris muscles of the anterior thigh. The medial malleolus is the medial and distal portion of the tibia. The fibula is thinner and lateral to the tibia. It is considered a non-weight-bearing bone. The proximal fibula head is a site of muscle attachment. The distal end of the fibula terminates at the lateral malleolus. The talus sits in between both malleoli. The foot and ankle are made up of 26 bones, held together by many ligaments (Figure 8.12). The foot is divided into 3 distinct areas. The hindfoot (calcaneus and talus) connects the foot to the lower leg. Dorsi and plantar flexion result from the gliding of the tibia over the talus. The midfoot includes the cuboid, navicular, and the 3 cuneiform bones (medial, intermediate, and lateral). It forms the arches of the foot, which function in shock absorption during gait. These 7 bones are sometimes referred to as the tarsal bones (tarsus). The forefoot consists of the remaining long bones of the foot (5 metatarsals, 5 proximal, 4 middle, and 5 distal phalanges). Notice the first metatarsal is much larger than the others. The size of this bone reflects its importance in weight bearing, especially during walking. Toes 2–5 are composed of 3 separate phalangeal bones while the first toe is only composed of 2 phalangeal bones (no middle phalanx). Key Muscles and Nerve Innervation gastrocnemius soleus plantaris popliteus flexor hallucis longus flexor digitorum longus tibialis posterior peroneus (fibularis) longus peroneus (fibularis) brevis quadratus lumorum tibialis anterior extensor hallucis longus extensor digitorum longus peroneus tertius tibial (S1,2) tibial (S1,2) tibial (L4,5 S1) tibial (L4,5, S1) tibial (L5,S1.2) tibial (L5, S1) tibial (L5, S1) superficial peroneal (L4,5, S1) superficial peroneal (L4,5, S1) T12, L1 deep peroneal (L4,5, S1) deep peroneal (L4,5, S1) deep peroneal (L4,5, S1) deep peroneal (L4,5, S1) The Leg and Ankle • • • • • • • • • • 2.3.1 Introduction to the leg and ankle (1:19) 2.3.2 Bones and ligaments of the ankle joint (4:14) 2.3.3 Bones and ligaments of the hindfoot (4:55) 2.3.4 Pulley-like structures around the ankle joint (1:40) 2.3.5 Review of bones, joints, and ligaments of the ankle region (1:46) 2.3.6 Ankle extensor and flexor muscles (5:20) 2.3.7 Fascial compartments of the leg (3:40) 2.3.8 Foot evertor and invertor muscles (4:08) 2.3.9 Review of muscles that move the ankle and foot (1:19) 2.3.11 Nerves of the leg and ankle (2:31) 2.3.12 Review of blood vessels and nerves of the leg and ankle (1:12) The Foot • • • • • • • • • • • • • 2.4.1 Bones of the midfoot, forefoot, and toes (2:49) 2.4.2 Main ligaments supporting the arches of the foot (2:28) 2.4.3 Plantar aponeurosis and metatarsophalangeal joints (4:14) 2.4.4 Review of bones, joints, and ligaments of the foot (1:00) 2.4.5 Long and short toe extensor muscles (3:24) 2.4.6 Long toe flexor muscles (2:38) 2.4.7 Short toe flexor muscle groups (3:14) 2.4.8 Short flexor muscles of the great and fifth toes (3:00) 2.4.9 Overview of short plantar muscles (1:57) 2.4.10 Review of muscles of the foot (1:15) 2.4.12 Nerves of the foot (4:01) 2.4.13 Review of blood vessels and nerves of the foot (0:53) 2.4.14 Skin of the foot (0:50) Tarsals Talus, calcaneus, navicular, first cuneiform, second cuneiform, third cuneiform, and cuboid Metatarsals: Base, Shaft, Head Phalanges: distal, middle, and proximal. 1. Gastrocnemius a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 2. Soleus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 3. Plantaris a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 4. Popliteus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 5. Flexor hallucis longus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 6. Flexor digitorum longus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 7. Tibialis posterior a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 8. Peroneus (fibularis) longus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 9. Peroneus (fibularis) brevis a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 10. Tibialis anterior a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 11. Extensor hallucis longus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 12. Extensor digitorum longus a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: 13. Peroneus tertius a. b. c. d. Origin: Insertion: Nerve innervation: Action: \ Dermatomes and Peripheral Nerves of the Lower Extremity Nerves of the Lower Extremity Nerve Sciatic nerve Common fibular (peroneal) Superficial fibular Deep fibular Tibial Superior Gluteal Inferior Gluteal Plantar Femoral Obturator Saphenous Posterior cutaneous Femoral Lateral and anterior Femoral cutaneous Sural Nerve Root Level Muscles Innervated and Sensory Area Innervated